Facing progressive hair loss can be deeply distressing, leaving many searching for permanent solutions. The moment you consider hair replacement surgery, the crucial questions emerge: Will the investment justify the high hair replacement cost? What advanced techniques, like FUE or DHI, ensure the safest hair replacement process? And most importantly, will the final, long-term before and after results genuinely restore your confidence and look undetectable? Understanding the science, differentiating non-surgical options, and vetting your hair replacement clinic are essential steps before making this life-changing commitment. Follow with Tran Plastic Surgery
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Surgical Hair Replacement: The Scientific Foundation

Hair replacement surgery often searched under terms like “surgical hair replacement” or “hair transplant” is an advanced field of cosmetic microsurgery aimed at permanently restoring hair for individuals experiencing hair loss or baldness. This procedure is a complex medical process, demanding precision in follicle extraction techniques and artistry in aesthetic design.
1. Hair Transplant vs. Non-Surgical Hair Replacement
A clear distinction between “Hair Transplant” (surgical) and “Hair Replacement” (non-surgical systems) is essential for patients considering their treatment options.
Hair transplant surgery is a medical procedure where a surgeon moves healthy hair follicles from the back or sides of the head (the donor area) to the balding area (the recipient area). The ultimate goal is to increase hair density and improve thickness. Because it uses the patient’s own follicles, the result is considered relatively permanent, as the transplanted follicles will continue to grow throughout their lifetime.
In contrast, the term “Hair Replacement” often refers to non-surgical solutions, such as hair systems or custom-made hairpieces. The primary advantage of these hair replacement hair systems is that they are significantly less expensive than surgical hair restoration initially. However, these non-surgical solutions require regular maintenance or periodic replacement over time. Thus, autologous hair transplant surgery is positioned as a long-term medical investment, distinctly different from the recurring maintenance costs of temporary hair replacement systems.
2. The Biological Mechanism of Autologous Hair Transplant
The success of autologous hair transplant surgery is rooted in the principle of “donor area dominance.” Most hair loss cases treated by transplantation are due to Androgenetic Alopecia (Male/Female Pattern Baldness), a very common genetic condition. This condition occurs when the male hormone Testosterone converts into 5-Dihydrotestosterone (5-DHT), which shrinks hair follicles in the front and crown areas in genetically susceptible individuals.
The hair follicles harvested from the occipital (back) or temporal (sides) areas are healthy, possessing a genetic resistance to the effects of 5-DHT. When these DHT-resistant follicles are moved to the balding area, they retain their inherent biological properties and continue to grow healthily and permanently. This scientific principle contributes to the high success rate of autologous hair transplant surgery, often reported up to 95%.
3. Who Is an Ideal Candidate for Hair Replacement Surgery?
Hair replacement surgery is not a universal solution for all types of hair loss. The ideal candidate must meet strict medical criteria to ensure safe and effective long-term results. If you are searching for a hair replacement near me, ensure the consultation covers these criteria.
Key Candidate Criteria include:
- Sufficient Donor Health: The patient must have enough healthy hair in the donor area to relocate to the recipient area. This donor hair must not be affected by current or future hair loss.
- Scalp Viability: The thinning/balding area of the scalp must still be capable of sustaining hair growth.
- Hair Loss Type: The procedure is best suited for genetic hair loss (Androgenetic Alopecia).
- Overall Health: The patient must be in good general health to undergo the procedure safely.
Considerations and Non-Candidates include:
- Hair replacement for women with diffuse hair loss across the entire scalp, as they often lack a sufficiently robust donor area for effective transplantation.
- Individuals experiencing hair loss due to medical treatments, such as chemotherapy.
- Those with a history of forming keloids (thick, fibrous scars) after injury or surgery.
Furthermore, extreme caution is required for younger patients, especially those under 25. While hair loss is most common in individuals aged 30–40, it can begin earlier. A skilled specialist at a reputable hair replacement clinic must plan the hairline and graft density, accounting for the patient’s predicted future hair loss progression. Setting realistic expectations is also a mandatory criterion for ensuring post-procedure satisfaction.
Modern Hair Replacement Techniques: FUE, DHI, and Beyond
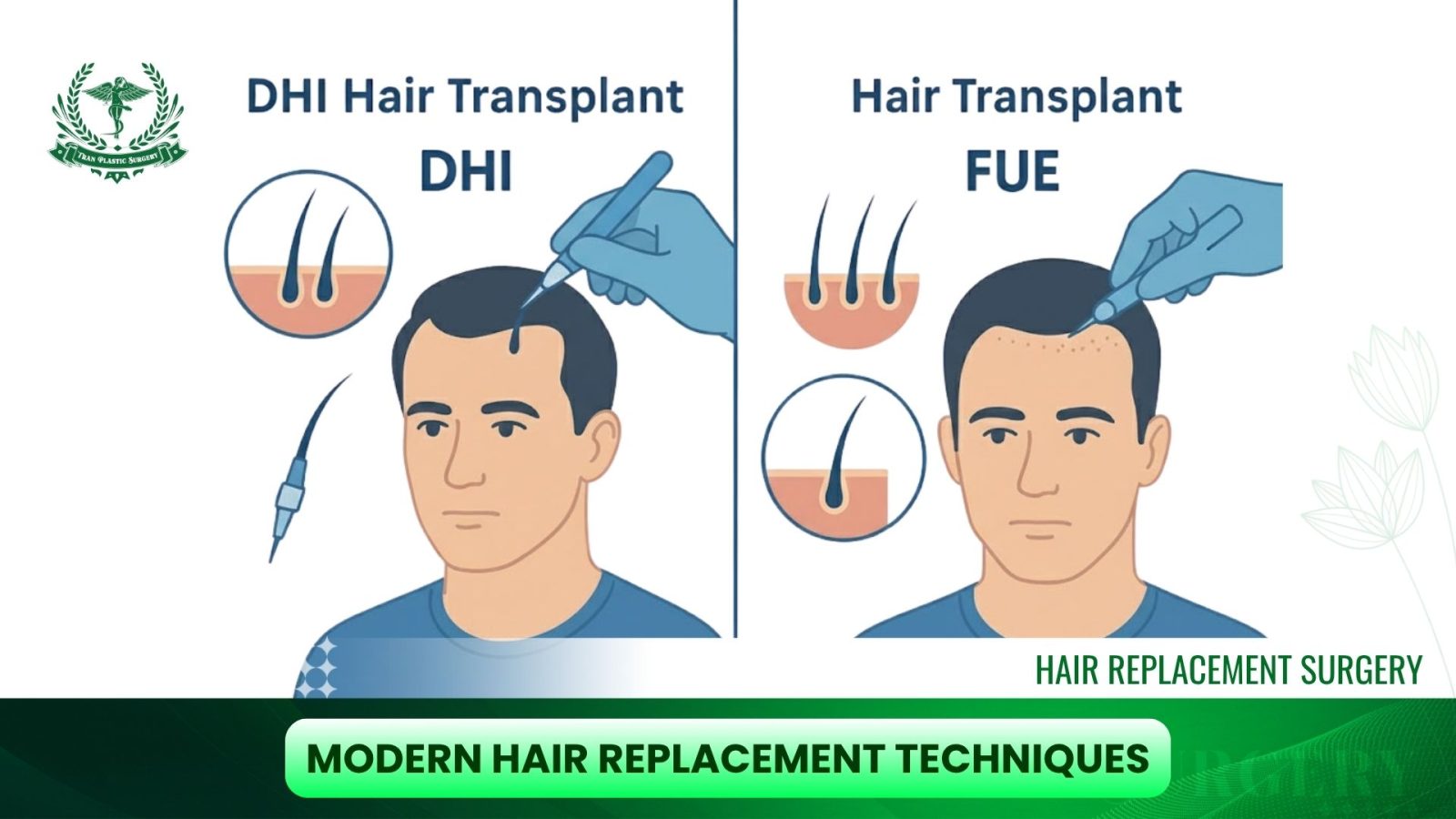
Advances in technology have led to several distinct methods, each offering specific pros and cons regarding invasiveness, graft survival rate, and scar aesthetics. These represent the best hair replacement treatment options today.
1. The Traditional Method: FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)
FUT, or Follicular Unit Transplantation, is the traditional technique that involves an excisional surgery.
- Mechanism: This technique involves surgically removing a thin strip of scalp from the donor area, typically the back of the head. After the strip is removed, the incision is sutured, resulting in a visible linear scar. Technicians then meticulously dissect this strip into individual follicular units under microscopes for grafting preparation.
- Advantages: FUT allows for the harvesting of a massive number of grafts in a single session, making it a preferred choice for patients with extensive hair loss requiring maximum coverage. The cost of FUT is also generally lower compared to the more modern methods.
- Disadvantages: The main drawback is the permanent, linear scar left in the donor area, which can be visible if the patient opts for short hairstyles.11 The donor area also requires a longer recovery time.
2. FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): The Less Invasive Trend
FUE marked a significant breakthrough, minimizing the invasiveness of surgical hair replacement.
- Mechanism: Instead of cutting a strip of tissue, FUE uses a micro-punch tool to individually extract each follicular unit directly from the scalp. This process is less painful due to its minimal invasiveness.
- Advantages: FUE hair replacement leaves no noticeable linear scar, only tiny, scattered puncture marks that are virtually invisible, allowing patients to choose shorter hairstyles. Donor area recovery is also quicker than with FUT.
3. DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) and Advanced Techniques
DHI hair replacement represents advanced microsurgical techniques, variations of FUE focused on maximizing graft survival rates and aesthetic control.
- DHI Mechanism: This technique utilizes a specialized implantation tool (the Choi Implanter Pen). DHI allows the hair follicle to be implanted directly into the recipient area immediately after harvesting, eliminating the need for a separate pre-made channel incision.
- DHI Advantages: Direct implantation minimizes the time the follicle spends outside the body, thereby significantly increasing the graft survival rate.17 The implanter pen gives the surgeon superior control over the angle, depth, and direction of hair growth, leading to a high-density, extremely natural-looking result. DHI can implant up to approximately 2500 follicular units in a single session, lasting 6–8 hours.
- Disadvantages: Due to the higher level of required precision, increased technical difficulty, and specialized equipment, DHI/Sapphire FUE typically has a higher hair replacement surgery price compared to traditional FUE and FUT.
4. Advanced Technology: Sapphire FUE and Robotics
To achieve the best hair replacement treatment results, technology continues to evolve, focusing on optimizing three core factors: density, survival rate, and naturalness.
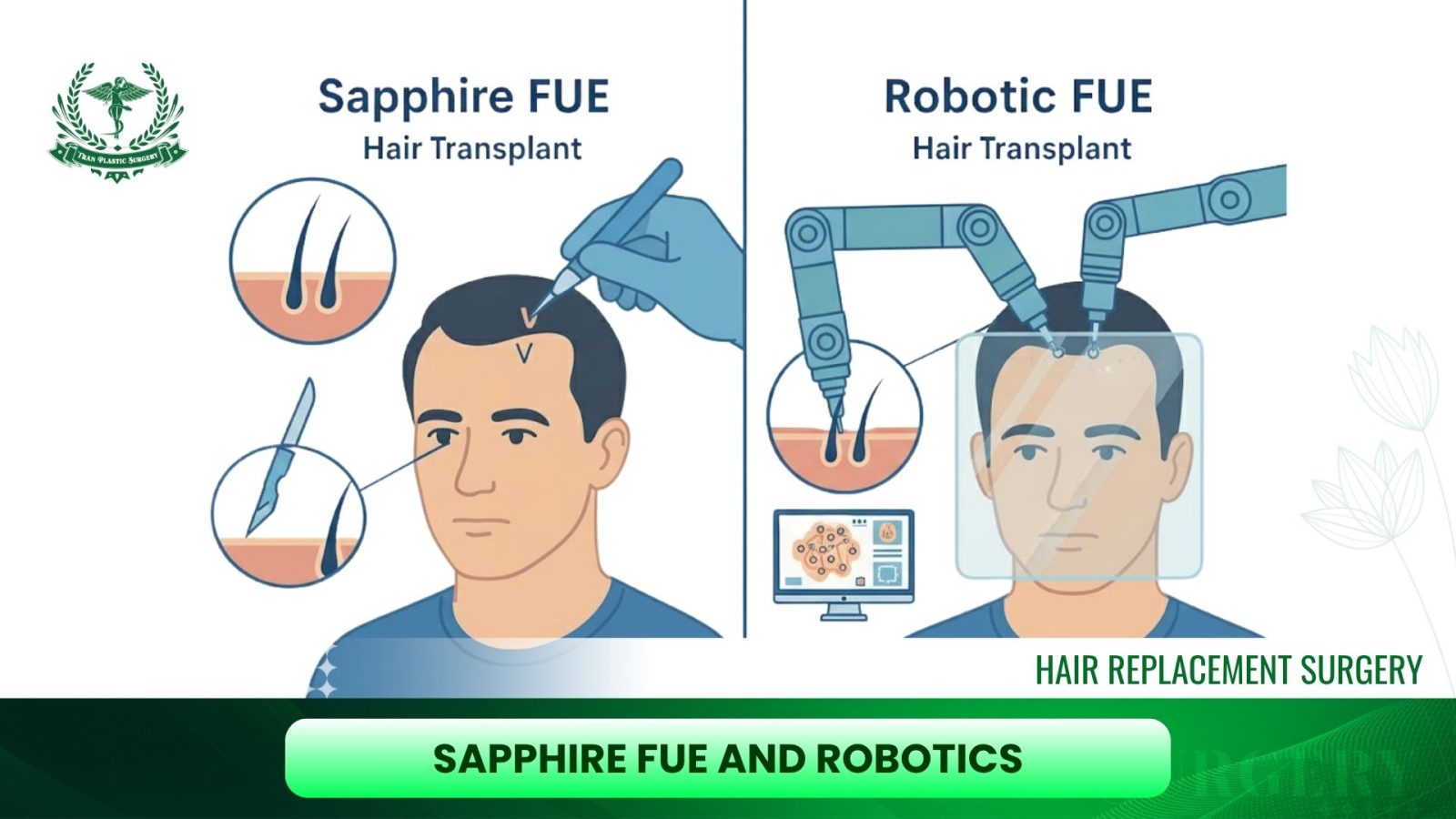
4.1. Sapphire FUE
Sapphire FUE enhances the traditional FUE method by employing blades made from real Sapphire stone instead of conventional steel in the channel creation phase.
The Sapphire blade is sharper and thinner, creating finer, more consistent incisions. This is crucial as it allows the surgeon to achieve higher hair density (potentially up to 4000 grafts in one session). Furthermore, the Sapphire material minimizes tissue trauma, retains sharpness longer, and possesses antimicrobial properties, helping reduce the risk of infection and promoting faster healing.
4.2. Robotic Hair Transplant
Robotic hair transplantation, such as the ARTAS IX system, uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) to automate specific steps of the FUE procedure.
- Robotic Advantages: This method offers increased speed, superior accuracy, and boasts a claimed graft survival rate of up to 99%. It is suitable for those seeking a highly automated and less surgeon-dependent process.
- Optimal Choice: DHI is considered the best hair replacement treatment option if the patient prioritizes the highest follicular survival rate and minimal scarring. Conversely, the Robotic method is suitable if the priority is a faster, highly automated process.
>>> You may be interested in: Direct Follicle Implantation: Costs, Results & Patient Reviews
Comparison of Autologous Hair Replacement Methods:
| Criterion | FUT (Strip Method) | FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) | DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) |
| Primary Mechanism | Cutting a strip of scalp | Individual follicle extraction | Direct implantation via Implanter Pen |
| Scar Type | Linear scar (visible if hair is short) | Tiny, scattered dots (virtually invisible) | No noticeable scarring |
| Graft Volume | Very High (suitable for severe baldness) | Medium to High | Maximum 2500 units/session |
| Graft Survival Rate | Relatively High | High | Very High (Often the highest) |
| Recovery Time | Longer | Faster (A few days) | Very Fast |
Gender Considerations: Hair Replacement for Men and Women
Hair replacement for men and hair replacement for women involves significant differences in hair loss patterns, candidate standards, and, crucially, in the aesthetic design of the hairline to ensure natural-looking results.

1. Hair Replacement for Men
Hair loss in men typically follows the Norwood pattern (localized thinning), creating distinct balding areas (primarily the forehead, temples, and crown), but usually maintaining a clearly defined and healthy donor area (occipital region).
When performing hair replacement men, the hairline design must create an angular shape, often a slight M-shape, with slightly receded temples . Surgeons must carefully calculate the angle and direction of growth for each follicle to achieve a masculine appearance that complements the facial bone structure. The main objective is to restore a sharp hairline and dense coverage in the affected regions. This requires a highly specialized hair replacement service.
2. Hair Replacement for Women
Hair loss in women is often more complex. Women commonly experience Diffuse Hair Loss following the Ludwig pattern, which makes identifying a healthy, stable donor area more challenging. As noted, women with hair loss distributed across the entire scalp are often not ideal candidates for a transplant.
- Techniques and Expectations: If indicated, surgeons may use mini-grafts harvested from a dense area and replanted in thinning areas to create a fuller look . It is critical to manage expectations transparently: surgery can camouflage thin areas and provide more fullness , but it is difficult to restore the pre-loss density entirely.
- Aesthetic Design: The female hairline requires a softer, lower contour, typically a rounded or U-shaped design . The focus is on maintaining a feminine appearance and avoiding noticeable recession at the temples . The distinct difference between male and female hairline design is a determining factor for achieving natural and long-lasting results appropriate to the patient’s facial proportions.
Analyzing the Hair Replacement Cost: An In-Depth View
The hair replacement cost is a substantial investment, generally fluctuating globally from $4,000 to $15,000 USD , not including medication and aftercare. This cost reflects the labor-intensive nature of the procedure and is driven by several quality-defining factors.
1. Key Cost Drivers
The hair replacement surgery price is not fixed and is determined by a pricing model based on quality, volume, and technique:
- Number of Grafts: This is the biggest determining factor. The cost increases proportionally with the number of grafts required. Pricing is often calculated per follicular unit. The severity of hair loss dictates a higher graft requirement, significantly increasing the cost. For example, a 5000-graft procedure can cost $13,000–$16,000 USD in the US.
- Transplant Technique: Modern methods requiring greater precision and complex equipment are more expensive. FUE and DHI/Sapphire FUE are priced higher than FUT. The average cost in the US for FUT is $5,975 USD, while FUE averages $6,684 USD. DHI and Sapphire techniques further elevate the price due to the demand for specialized microsurgical expertise and technology.
- Surgeon’s Reputation and Experience: Highly skilled surgeons, who ensure a high success rate (up to 95%) and safety, charge higher service fees. Choosing an experienced surgeon is an investment in the quality of the aesthetic outcome and patient safety.
- Geographical Location and Facility Standards: The clinic’s operating costs influence the total price. Clinics in regions with higher living costs (e.g., the US, Australia) often have significantly higher prices than medical tourism centers (e.g., Turkey). A modern, licensed medical environment also increases the cost but ensures hygiene and minimizes the risk of infection .
2. Understanding “How Much Does Hair Replacement Surgery Cost?”
Patients should always seek transparency in the cost structure. While some international clinics may offer all-inclusive packages instead of charging per graft, understanding the fundamental cost per graft is essential for comparing service quality.
Warning Against Low Cost: Hair replacement is a sophisticated procedure requiring precision and advanced technology. Therefore, an unusually low price (e.g., very cheap package deals) should be considered a serious warning sign (Red Flag). Low prices may reflect the use of outdated equipment, poor hygiene standards, or inexperienced teams, all of which increase the risk of complications and poor results . The difference in cost between advanced methods (DHI/Sapphire) and traditional methods reflects the investment in graft survival rates and aesthetic density.
| Factor | Impact on Total Cost | Details and Considerations |
| Severity of Baldness | Directly proportional (more severe, more grafts needed) | Cost is usually calculated per follicular unit (graft) |
| Transplant Technique | FUE/DHI/Sapphire > FUT | Advanced techniques require higher technology and expertise |
| Surgeon Reputation | Highly skilled surgeons charge higher fees | Ensures the highest success rate and safety |
| Facility Standards | Higher cost at modern, medically certified clinics | Minimizes the risk of infection and complications |
The Hair Replacement Process: A Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
The hair replacement process is a standardized sequence of steps, beginning with meticulous planning and concluding with rigorous post-operative care.
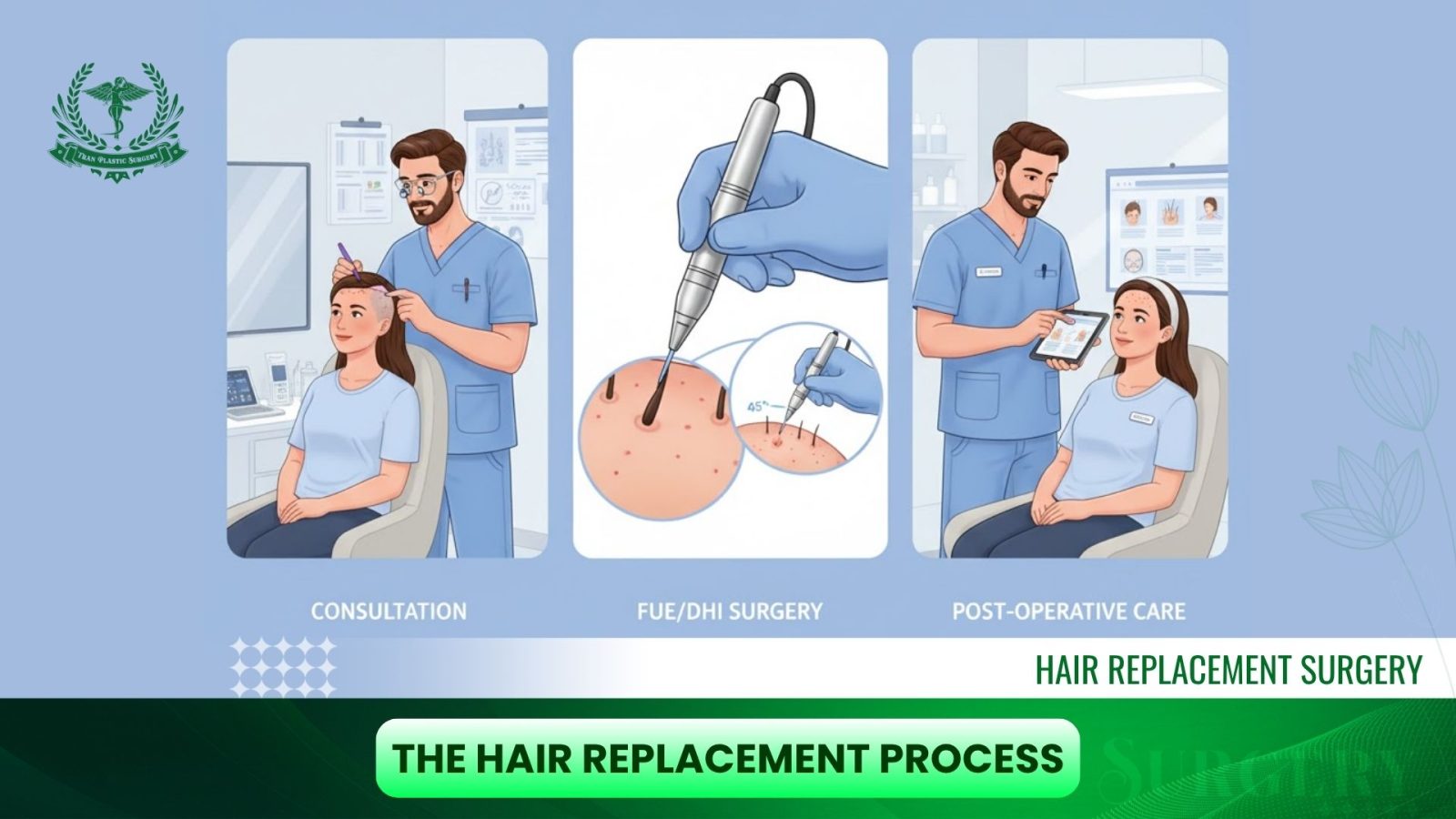
1. Pre-Surgical Phase: Establishing the Personalized Plan
- Consultation and Medical Assessment: The surgeon conducts a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, current hair loss pattern, and donor area capacity. This step is mandatory to confirm if the patient is a suitable candidate.
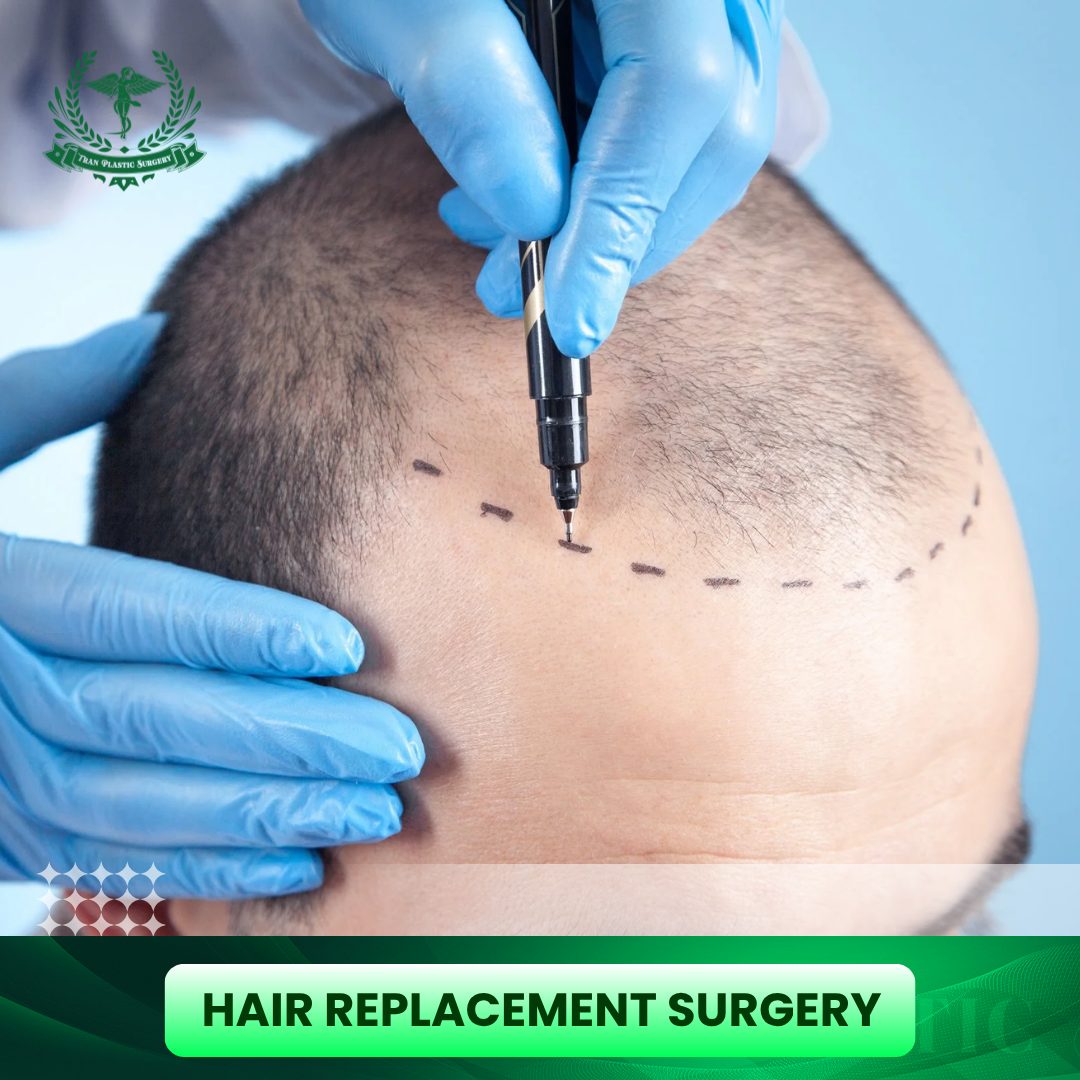
- Hairline Design: This is the most crucial aesthetic phase. The surgeon draws and plans the frontal hairline, ensuring it is harmonious with the patient’s face shape and gender (angular for men, rounded for women). The design must account for future hair loss progression for long-term naturalness and sustainability.
- Preparation: Hair in the donor area is usually shaved short to facilitate follicle extraction (especially in FUE/DHI).
2. Surgical Phase (Performing FUE/DHI)
A typical FUE procedure lasts approximately 5 to 8 hours, depending on the number of grafts.
- Anesthesia: The donor and recipient areas are sanitized. Local anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure. Mild sedatives may also be used to enhance comfort.
- Follicle Extraction (Harvesting): The surgeon uses a microsurgical device to extract healthy individual follicular units from the donor area. These grafts are then sorted and counted.
- Channel Incision or Direct Implantation:
- FUE/Sapphire FUE: The surgeon creates micro-channels in the recipient area. This stage demands extremely high precision, as the angle, frequency, and depth of the channels determine the natural growth direction of the hair (typically angled at 45–50 degrees).
- DHI/HAT: The surgeon uses a specialized implanter pen to directly implant the follicle into the scalp, combining the channel creation and grafting steps simultaneously.
The channel creation/direct implantation phase is the factor determining the final aesthetic result. This step should be performed by the highly skilled surgeon, not just technicians, to ensure the hair grows naturally, avoiding undesirable outcomes.
3. Post-Surgical Care (Crucial for Graft Survival)
Post-operative care is the most critical stage, directly impacting the development of new hair follicles.
- Initial Recovery: Patients can typically be discharged after a 30-minute post-operative monitoring period. Mild swelling, redness, and discomfort are normal for the first two days. Most patients require only 2–5 days of rest for basic activities, but 1–2 weeks of adequate rest at home is recommended to promote optimal healing.
- Cleaning and Protection: The doctor will provide detailed instructions on how to wash hair replacement surgery areas and measures to protect the grafts. Strict adherence to these guidelines is necessary to ensure a high graft survival rate.
Real Before/After Results and the Hair Growth Timeline
Autologous hair transplant provides permanent, long-lasting results because the transplanted follicles will continue to grow like normal hair.5 However, achieving the final result is a journey that requires patience.
1. Hair Transplant Growth Timeline
The hair growth process after transplantation takes about one year (10–12 months) to achieve full density.
- Week 1 (Healing): Scabs form on the recipient area and begin to shed naturally.
- Weeks 2 – 4 (Temporary Hair Shedding – Shock Loss): This is the most crucial stage for managing expectations. The transplanted hairs will fall out; this phenomenon is completely normal and a natural reaction of the follicles to the micro-trauma of the procedure. Shock loss occurs in almost all patients, usually peaking around weeks 4–5. Understanding that shedding is a sign that the hair is entering a resting phase before regrowth is essential to prevent patient anxiety.
- Months 1 – 3 (Early Growth): Soft, thin “baby hairs” begin to appear.
- Months 4 – 6 (Thickening): Hair density noticeably improves. The new hair grows back stronger and thicker.
- Months 7 – 9 (Maturation): Coverage increases, and the hair looks fuller.
- Months 10 – 12 (Final Result): Maximum density and natural appearance are achieved. The complete result can continue to improve up to 18 months.
| Time After Transplant | Key Phenomenon | Result Expectation and Note |
| Days 1-7 | Wound healing, scab shedding | Gentle washing, absolute protection of the grafted area |
| Weeks 2-4 | Temporary Hair Shedding (Shock Loss) | Transplanted hair falls out. This is a completely normal reaction |
| Months 4-6 | Baby hairs grow, noticeable thickening begins | Density improves; results become visible. |
| Months 10-12 | Final Results Achieved | Hair is fully mature, maximum density, and natural growth is established. |
2. The Permanence of Hair Transplant Results
The result of autologous hair replacement surgery is durable and long-lasting because the transplanted follicles are resistant to the 5-DHT hormone that causes hair loss. After transplantation, the hair can still grow long, be dyed, and develop like natural hair.
However, it should be noted that the result may still be affected by age and genetic factors only for the remaining natural hair (the hair that was not transplanted) over time. For this reason, strategic surgical planning of the hairline from the outset is paramount.


Choosing a Reputable Hair Replacement Clinic
Selecting a reputable hair replacement clinic is a crucial factor determining the success, safety, and aesthetic quality of the final outcome.
1. Expertise and Facility Standards
- Highly Specialized Medical Team: Hair transplant surgery requires a surgeon with extensive experience and high specialization, not only in extraction but also in the art of hairline design. An experienced surgeon ensures accurate diagnosis and safe, effective procedure execution. Patients should verify that the surgeon holds proper certifications and directly performs the critical stages of the procedure (not just technicians).
- Modern and Safe Facilities: The clinic must be a licensed medical facility (e.g., licensed by the Ministry of Health). The premises must be modern, clean, and well-maintained. Choosing a clinic with medically certified surgical rooms and stringent infection control is a mandatory condition to minimize the risk of complications and infection.
- Adoption of Advanced Technology: Reputable clinics typically employ advanced technologies like DHI, Sapphire FUE, or Robotics, which enhance the precision of the transplant process, minimize invasiveness, and increase the success rate.
2. Red Flags to Avoid When Searching for “Hair Replacement Near Me”
To protect their investment and health, patients need to be wary of several common warning signs:
- Prices That Seem Too Low or Lack Transparency: A hair replacement surgery price significantly lower than the market average for reputable clinics is a warning sign about quality. Quality medical expertise and advanced technology come with a reasonable cost
- Unrealistic Promises: A trustworthy clinic will always set realistic expectations based on the patient’s current hair status and donor capacity. Be wary of promises of “unimaginable” graft counts, “perfect” unnatural hairlines, or instant results .
- Skipping the Consultation Process: Personalized consultation is the foundation of successful hair replacement surgery. If a clinic fails to take the time to detailedly assess your medical history, hair loss pattern, or does not explain why a specific method (FUE, DHI) is chosen, this is a serious red flag.
The clear difference between a reputable clinic and a lower-quality facility lies in its ability to set realistic expectations and maintain transparency at every stage, from initial assessment to managing the post-Shock Loss recovery process.
Conclusion and Professional Recommendation
Autologous hair replacement surgery is an effective and long-term medical solution to permanently address hair loss, significantly superior to temporary hair replacement systems. . The transplant uses DHT-resistant follicles, ensuring permanent results with a high success rate.

The development of microsurgical techniques like DHI and Sapphire FUE has increased the precision, graft survival rate, and natural appearance of the hairline, which is particularly vital for aesthetic design in both men and women. The hair replacement cost reflects the technical complexity and the surgeon’s experience. Choosing advanced methods, although costlier initially, is an investment in aesthetic quality, shorter recovery time, and long-term safety.