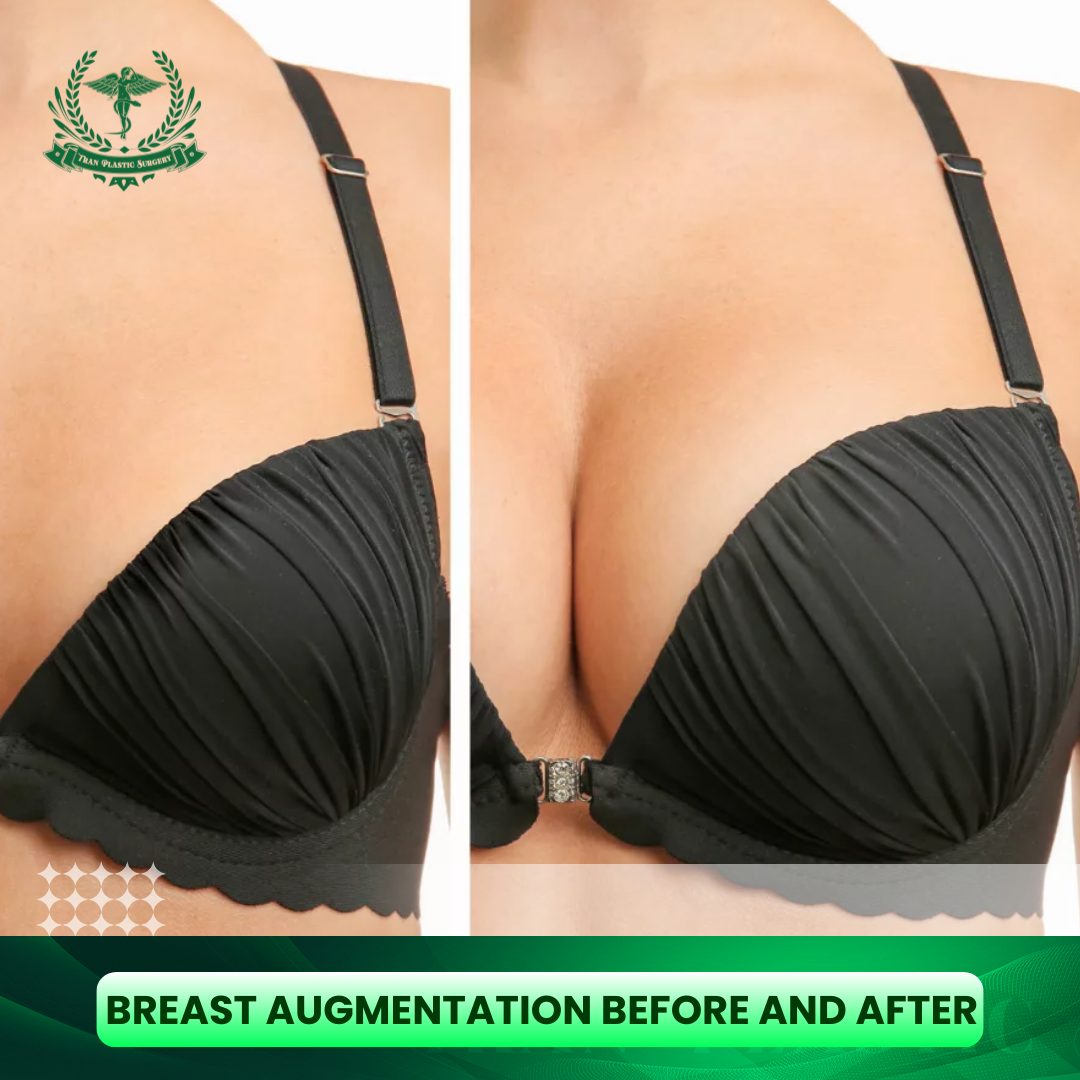
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide, prompting many to consider hair transplant surgery as a solution for restoring hair and confidence. While hair transplants can offer excellent results, it is crucial for patients to understand the hair transplant risk, potential side effects, and safety considerations before undergoing the procedure. This guide provides detailed information to help patients make informed decisions, covering everything from common risks to rare complications, factors affecting safety, and tips to ensure a successful outcome.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Hair Transplant Procedures
Hair transplant surgery involves relocating hair follicles from areas of dense growth (usually the back and sides of the scalp) to thinning or bald areas. The procedure has evolved significantly, and two primary techniques dominate the field today:
1. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a minimally invasive procedure where individual hair follicles are removed and transplanted to the recipient area. Benefits include:
- Minimal scarring
- Faster recovery times
- Lower post-operative discomfort
FUE is considered safer for patients who want smaller, precise sessions. Many patients ask, is FUE hair transplant safe? Studies and clinical experience suggest that when performed by trained professionals, FUE is safe with low complication rates.
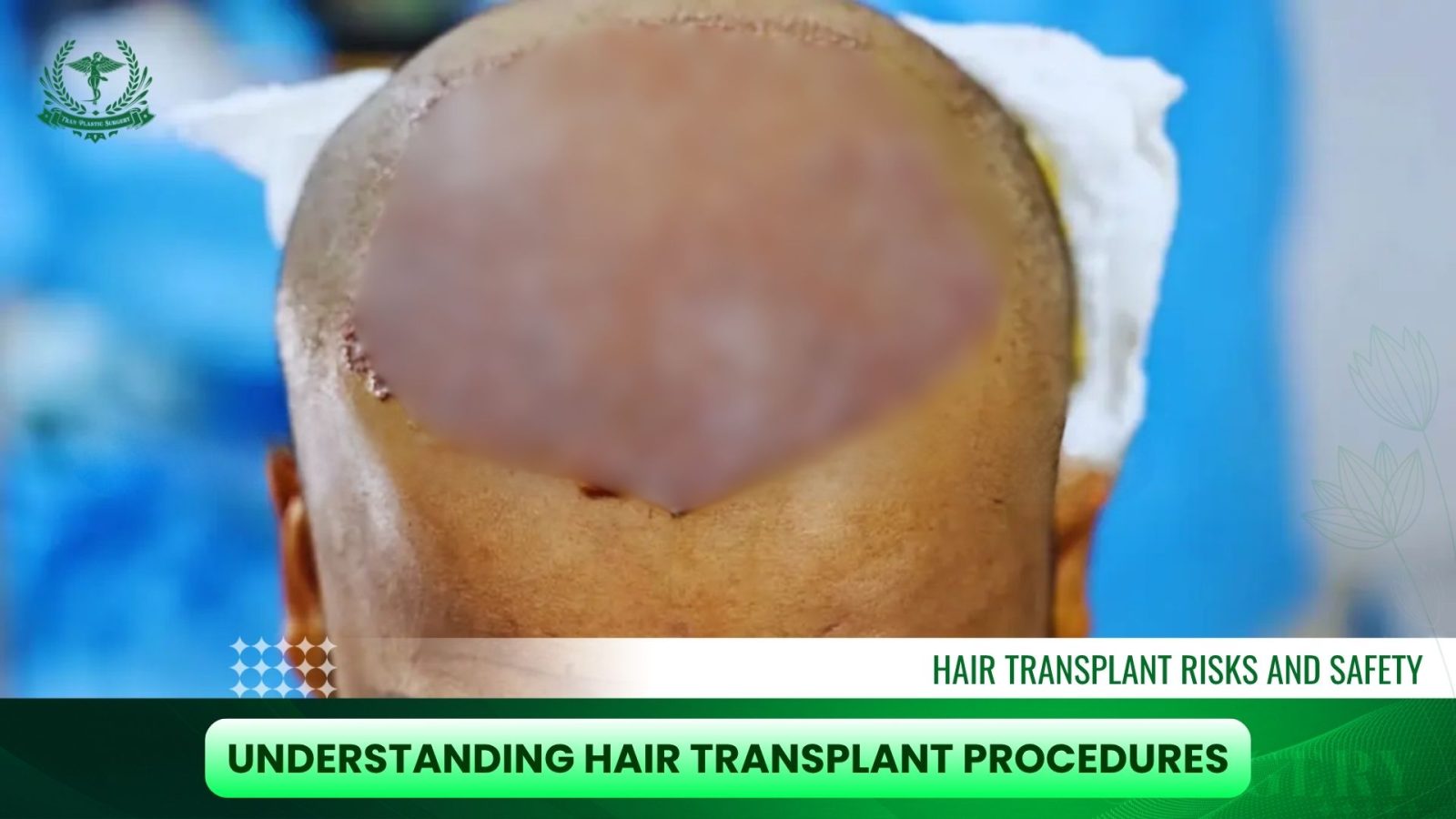
2. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, from which hair follicles are harvested. This technique is suitable for larger sessions but leaves a linear scar. FUT carries a slightly higher risk of post-operative discomfort compared to FUE but remains a reliable method for patients with extensive hair loss.
Both FUE and FUT procedures are safe when conducted in a sterile surgical environment with experienced surgeons. Understanding the method used is important for patients to anticipate recovery and potential risks.
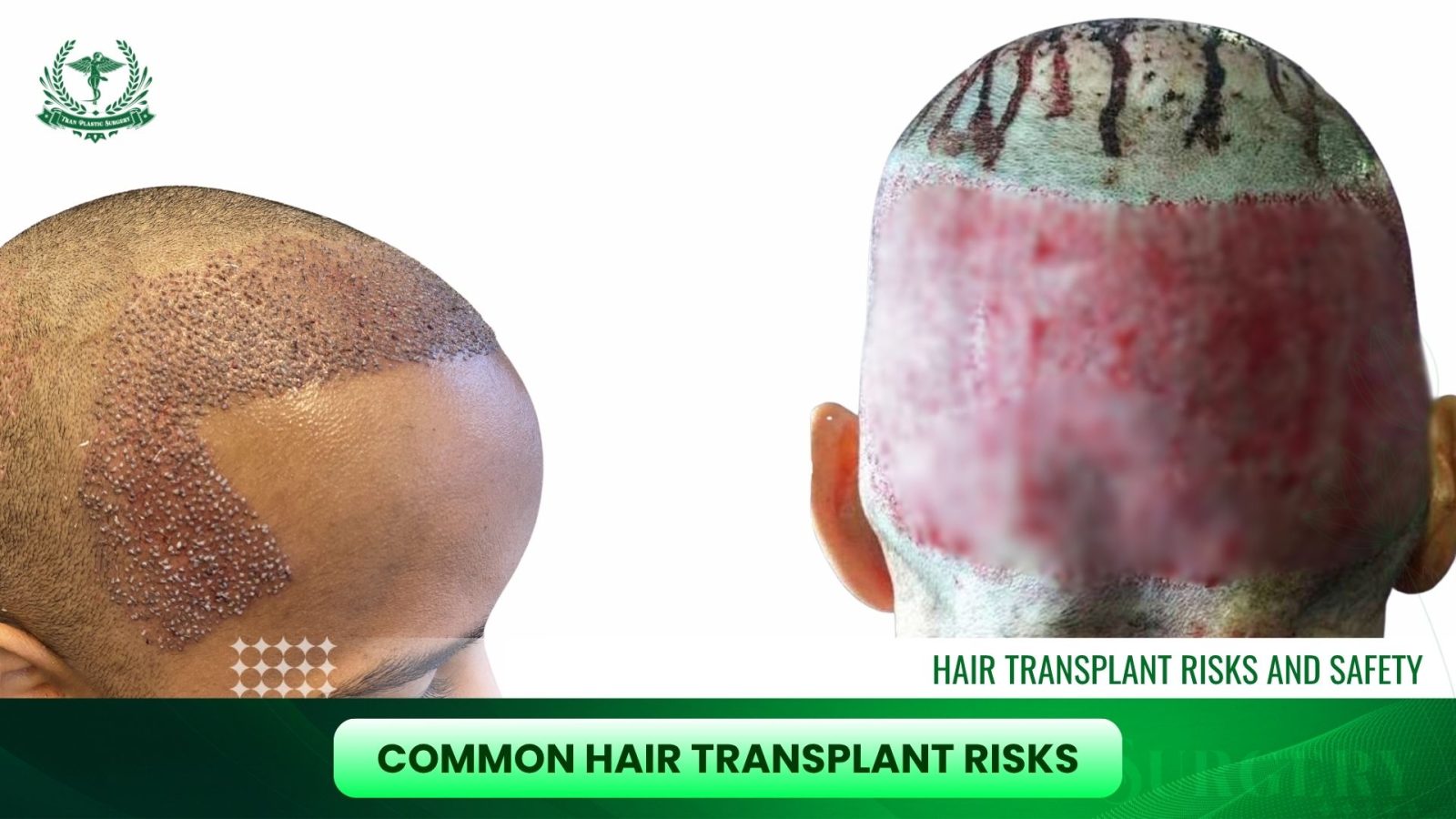
Common Hair Transplant Risks
Hair transplant surgery is generally low-risk, but like any surgical procedure, complications can occur. Patients should be aware of these potential issues to manage expectations and take preventive measures.
1. Infection
Infection is one of the most common concerns after surgery. While strict sterile techniques significantly reduce this risk, patients must follow post-operative care instructions carefully. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, or pus around the grafts. Early intervention with antibiotics can prevent serious complications.
2. Bleeding and Scarring
Minor bleeding is common during and after the procedure. Scarring varies by technique:
- FUE: Small, dot-like scars are usually barely visible
- FUT: Linear scars can form at the donor site
Proper post-surgical care, including keeping the area clean and avoiding excessive physical activity, helps minimize scarring.
3. Graft Failure and Shock Loss
Not all transplanted follicles survive, leading to partial graft failure. Shock loss, where existing hair temporarily thins after the procedure, can also occur. While distressing, most hair regrows within months. Patients often ask, how long until hair transplant grafts secure? Typically, transplanted grafts stabilize within 7 to 14 days, with full results visible after 6 to 12 months.
4. Allergic Reactions and Anesthesia Risks
Hair transplant surgery typically uses local anesthesia. Although allergic reactions are rare, they can occur. Pre-operative screening ensures the safest anesthesia plan. Patients with a history of allergies should discuss this with their surgeon.
Read more:
- Top 19 Hair Transplant Myths – Debunked From Experts
- Why Am I Losing Hair? Common Causes & Hair Thinning Treatments
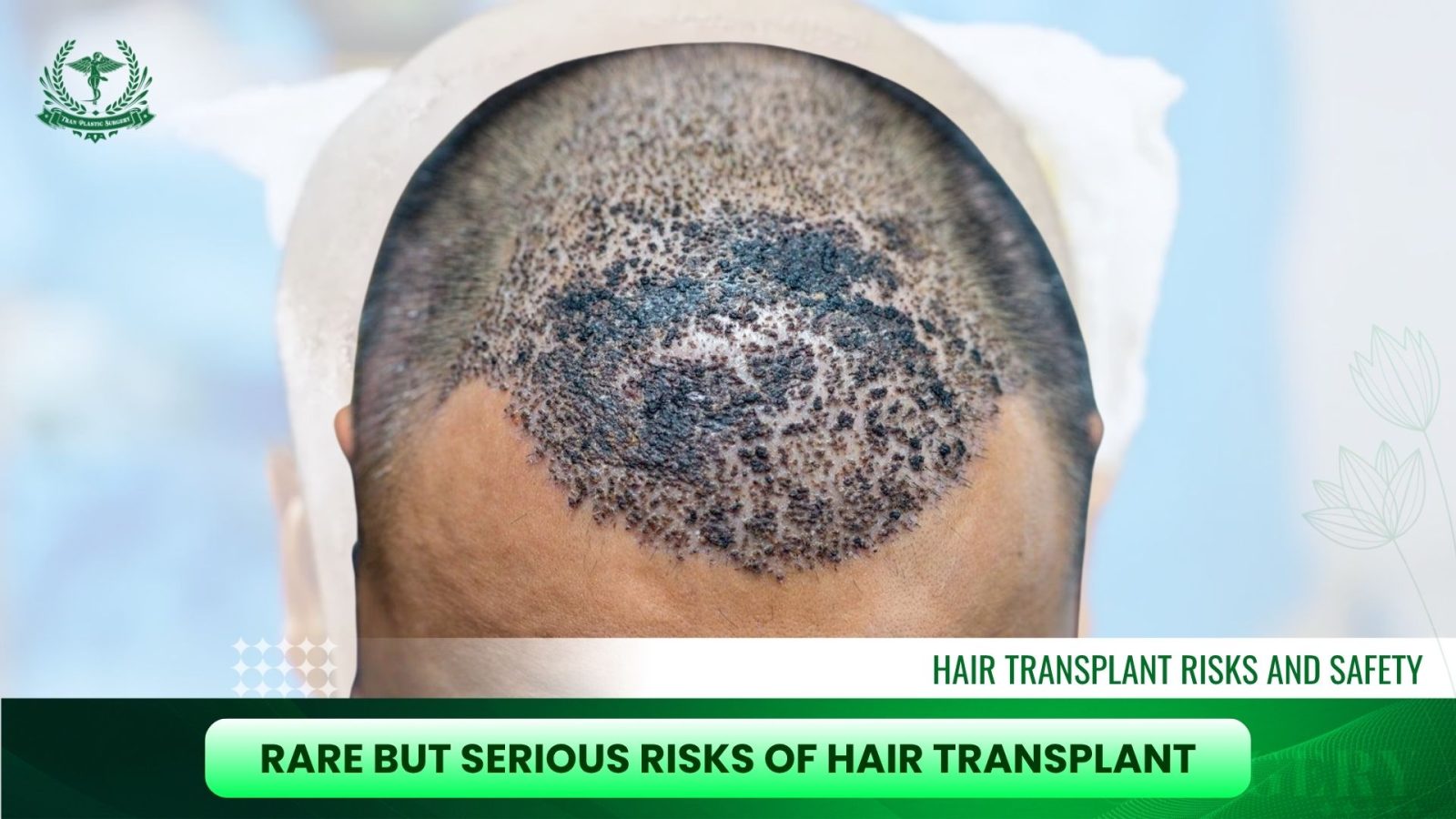
Rare but Serious Risks of Hair Transplant
Although rare, some complications can be more serious and should be understood by patients before surgery.
1. Can Hair Transplant Cause Cancer?
Concerns about cancer after hair transplant are common but unfounded. Hair transplant surgery involves only relocating hair follicles and does not introduce harmful substances or carcinogens. Current research confirms that hair transplants do not increase cancer risk.
2. Can Hair Transplant Cause Death?
Hair transplant surgery is considered a low-risk outpatient procedure. Fatal complications are extremely rare and are usually linked to severe allergic reactions or pre-existing medical conditions. Documented cases of death from hair transplant are virtually nonexistent. Patients often search, has anyone died from hair transplant? but evidence shows that with proper medical care, the risk is negligible.
Other Rare Complications
- Cyst formation: Occasionally, small cysts can develop around transplanted follicles. They are usually temporary and resolve naturally.
- Numbness or tingling: Temporary nerve irritation can occur in the donor or recipient area.
- Unnatural hair growth or density issues: Poor planning can lead to unnatural results, emphasizing the importance of experienced surgeons.
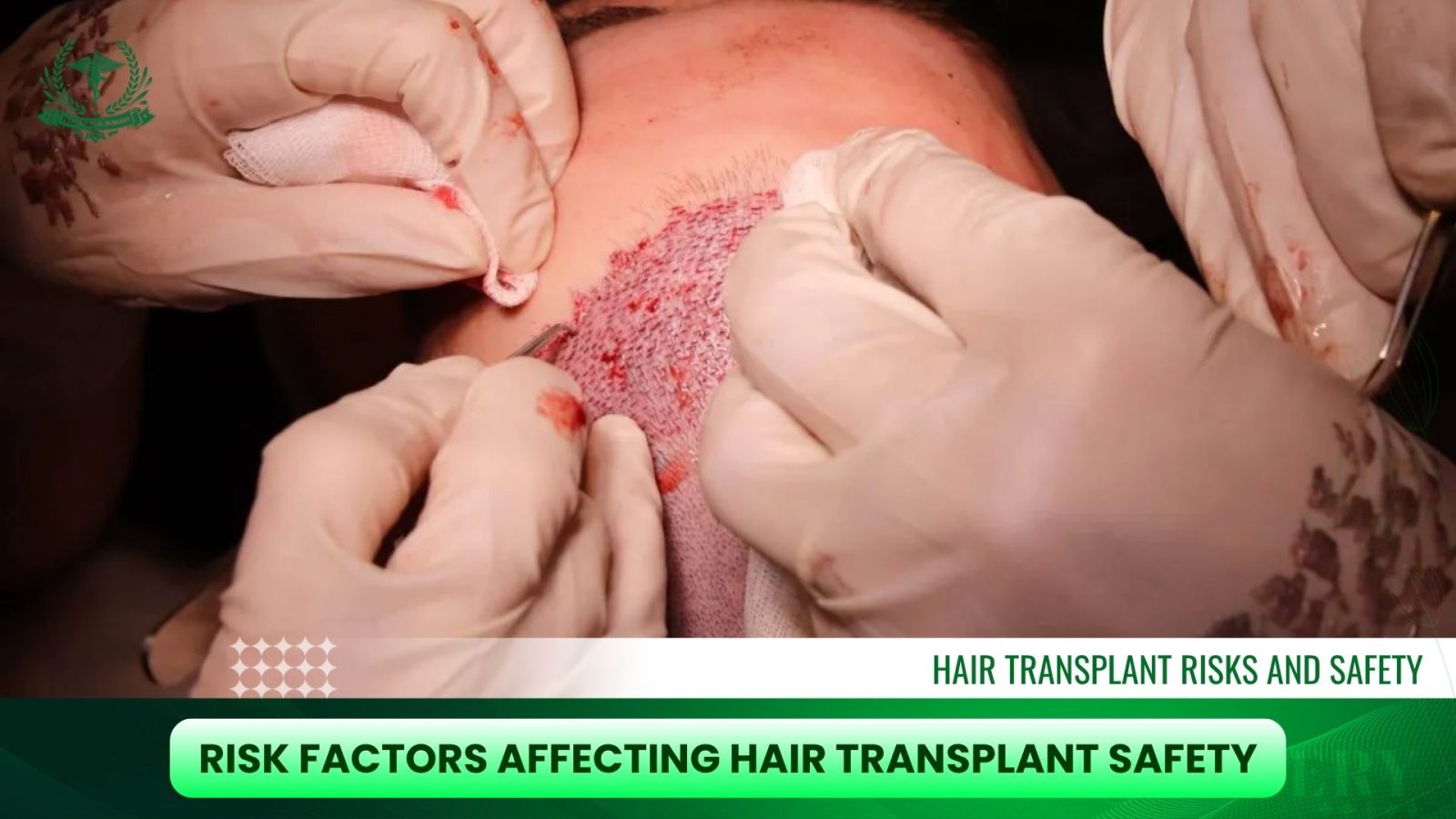
Risk Factors Affecting Hair Transplant Safety
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of complications, and patients should be evaluated individually to minimize hair transplant risk factors.
1. Age and General Health
Older patients or those with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, may experience slower healing and a slightly higher risk of complications.
2. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition can impair healing and graft survival. Quitting smoking at least two weeks before and after surgery is strongly recommended.
3. Medications and Supplements
Blood thinners, anti-inflammatory drugs, or certain supplements may increase bleeding risk. A full medication review before surgery is essential.
4. Surgeon Experience and Clinic Standards
Choosing a highly skilled surgeon and a clinic with stringent safety protocols reduces complications. The surgeon’s expertise affects not only the risk hair transplant but also the natural appearance and survival of grafts.
For the safest and most natural results, choose a surgeon you trust. Call Tran Plastic Surgery now at (714) 839-8000 or (714) 530-5888. Schedule a consultation for professional, personalized care (Directions).
Special Considerations for Patients
1. Can a Completely Bald Person Get a Hair Transplant?
Hair transplant success relies on sufficient donor hair. Completely bald patients with limited donor hair may not be suitable candidates. Alternative treatments, such as scalp micropigmentation or hair systems, may be considered in these cases.
2. Does Hair Transplant Affect Existing Hair?
When performed correctly, hair transplant surgery does not damage existing hair. Temporary thinning may occur due to shock loss but typically resolves within a few months.
3. Gender-Specific Considerations
While hair transplants are often associated with men, women also experience hair loss. Female patients may face additional considerations, such as hormonal fluctuations and diffuse hair thinning, which can affect transplant planning and outcomes.
Tips to Minimize Hair Transplant Risks
Proper preparation and post-operative care are crucial for minimizing risks and achieving optimal results.
- Follow Pre-Operative Instructions: Avoid smoking, alcohol, and certain medications as advised.
- Maintain Hygiene: Keep the recipient and donor areas clean to prevent infection.
- Avoid Physical Strain: Limit heavy exercise and contact sports during the initial healing period.
- Follow Medication and Care Guidelines: Take prescribed antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or hair growth stimulants as instructed.
- Monitor Healing Progress: Attend all follow-up appointments and report any unusual symptoms promptly.

Understanding Side Effects and Recovery
1. Swelling and Redness
Mild swelling and redness around the transplanted area are normal and usually resolve within a week.
2. Itching and Crusting
As grafts heal, itching and small crusts may form. Patients should avoid scratching to prevent dislodging grafts.
3. Long-Term Hair Growth Expectations
Hair growth occurs in phases:
- Initial shedding (2–3 weeks): Grafted hair may fall out temporarily
- Dormant phase (1–3 months): Follicles rest before producing new hair
- Growth phase (3–12 months): Gradual hair regrowth, with density improving over time
Understanding this timeline helps manage expectations and reduces anxiety about perceived hair loss post-surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hair Transplant Safety
1. Is Hair Transplant Safe for Everyone?
Most healthy adults are good candidates, but patients with certain medical conditions, poor donor hair, or unrealistic expectations may face higher risks.
2. Are There Long-Term Complications?
Long-term complications are uncommon. Some patients may notice slight donor area thinning or minimal scarring, but these issues are usually minor and manageable.
3. How Can Patients Ensure Safe Results?
Selecting a qualified surgeon, following pre- and post-operative instructions, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key to minimizing hair transplant risk.
4. Is FUE Safer Than FUT?
FUE generally carries slightly lower risks of scarring and discomfort, but both methods are safe when performed correctly. The choice depends on the patient’s hair loss pattern, donor availability, and surgical goals.
Conclusion
Hair transplant surgery is a safe and effective solution for hair restoration when performed by trained professionals. Understanding hair transplant risks, possible side effects, and factors affecting safety is essen. By educating yourself about hair transplant risks, recovery, and post-operative care, you can confidently approach hair restoration and enjoy lasting, natural results.
Don’t leave your hair restoration journey to chance. Get in touch with Tran Plastic Surgery for reliable answers and a safe, customized treatment plan.