Welcoming a newborn brings immeasurable joy yet for many women, it also triggers a sudden and distressing change: the moment when postpartum hair loss begins. If you’re concerned about thinning hair after childbirth and wondering about a hair transplant after pregnancy, you’re not alone and understanding the full picture is the first step toward renewed confidence.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Postpartum Hair Loss?
Postpartum hair loss, also known as telogen effluvium, is the excessive temporary shedding of hair that many new mothers experience a few months after childbirth.
It is caused by the dramatic drop in the hormones estrogen and progesterone following delivery. During pregnancy, high levels of these hormones keep a larger-than-normal amount of hair in the growth phase (anagen), making hair appear thicker. When hormone levels return to normal post-birth, all that extra hair rapidly shifts into the resting/shedding phase (telogen) and falls out.
The shedding usually starts around two to four months after giving birth and typically resolves on its own within six to twelve months.
When Does Postpartum Hair Loss Start?
The most common question you hear is precisely that: “When does postpartum hair loss start?” and the answer aligns perfectly with the hair’s natural growth cycle reacting to hormonal shifts. Here is a detailed breakdown of the timeline:
1. The Onset: 2 to 4 Months Postpartum
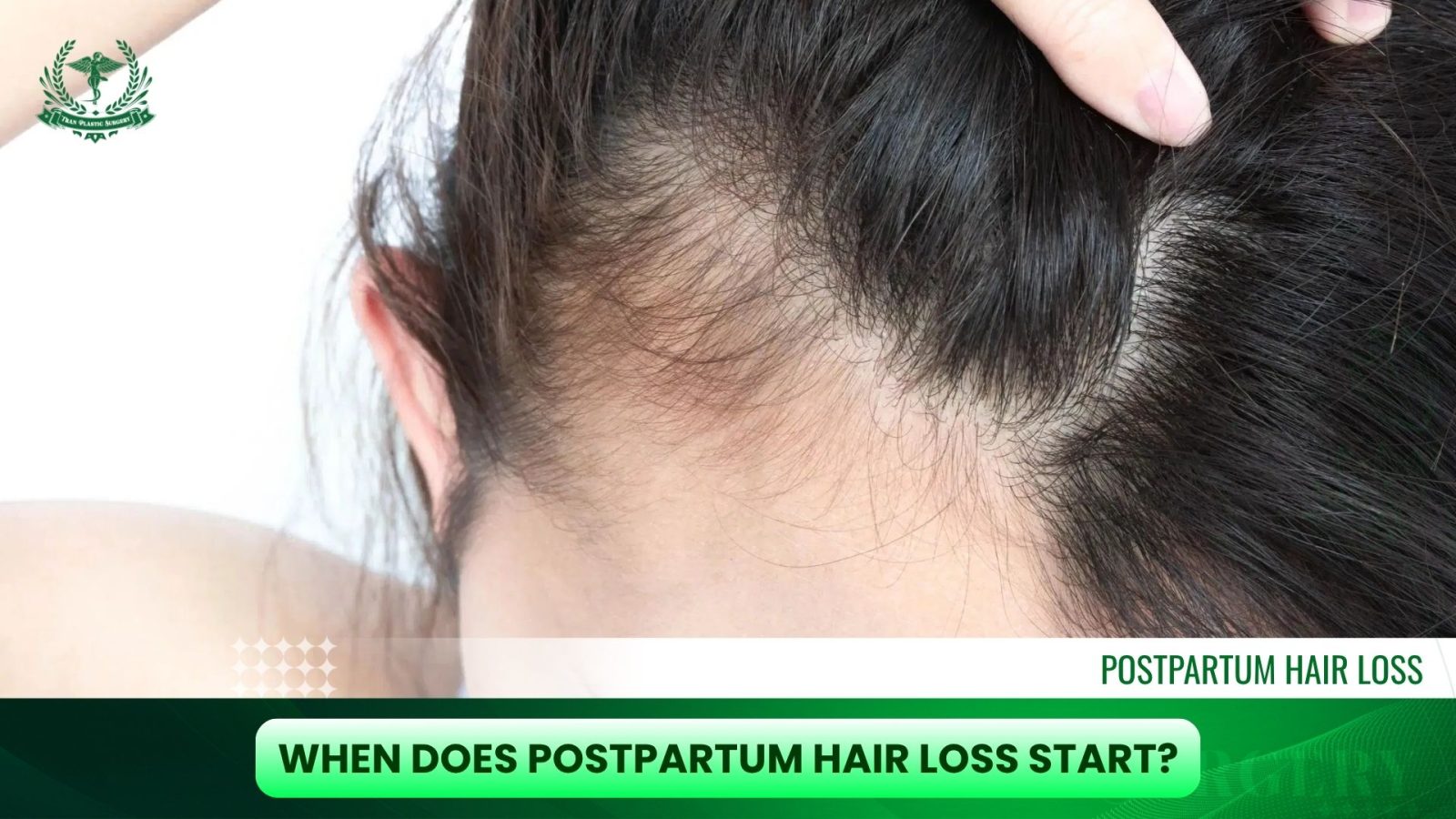
The Start: Most women begin to notice increased shedding around 2 to 4 months after delivery. This is when the large group of hair follicles that entered the resting phase (telogen) immediately post-birth are ready to move into the shedding phase (exogen).
Initial Signs: You may first see significant amounts of hair on your brush, on your pillow, or clogging the shower drain.
2. The Peak: 3 to 5 Months Postpartum
- Heaviest Shedding: The shedding typically peaks somewhere between 3 and 5 months postpartum.
- Severity: During this time, it is common to lose a noticeable amount of hair, sometimes up to 300 strands per day, compared to the normal loss of 50–100 strands. This heavy loss often causes visible thinning, particularly around the temples and the hairline (the “widow’s peak” area).
3. Resolution and Regrowth: 6 to 12 Months Postpartum
- Shedding Slows: For most women, the excessive shedding begins to slow down and stop by 6 months postpartum.
- Regrowth: Your hair’s growth cycle will usually return to its pre-pregnancy rhythm, and you will start to see new hair growth (often referred to as “baby hairs” or short, fuzzy new growth) from 6 to 12 months postpartum.
- Full Recovery: Your hair should largely return to its pre-pregnancy thickness by the time your child reaches 12 to 18 months of age.
4. When to Talk to a Doctor
While the timeline above is normal, you should consult a healthcare provider or a dermatologist if:
- The excessive hair shedding persists for more than 12 months after delivery.
- The hair loss is accompanied by other symptoms like extreme fatigue, weight changes, or palpitations, as this could indicate an underlying issue like a thyroid disorder or a nutritional deficiency (e.g., iron deficiency).
Do you want to know some myths about hair transplant? Don’t miss this article: Hair Transplant Myths Debunked From Experts
How to Limit Postpartum Hair Loss: Non-Surgical Strategies
1. Gentle Hair Care and Nutritional Support
While postpartum hair loss cannot be completely prevented, its severity can be managed:
- Avoid tight hairstyles, high-heat styling, or harsh chemical treatments.
- Use volumizing shampoos, lightweight conditioners, and consider a shorter haircut for added visual fullness.
- Ensure adequate intake of key nutrients:
- Biotin: strengthens hair follicles
- Folate (B9) & B12: support red blood cell production for scalp nutrition
2. Advanced Non-Surgical Treatments
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Uses the patient’s own blood to stimulate dormant follicles, improve scalp circulation, and promote regrowth. Visible improvement typically begins within 4–6 months.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Non-invasive laser therapy enhances blood flow and follicle activity, increasing hair density. Combining PRP with LLLT may offer optimal regrowth results.
These interventions are ideal for women awaiting the natural resolution of postpartum shedding or preparing for a hair transplant.

What To Do When Postpartum Hair Loss Becomes Chronic?
If your hair shedding persists beyond 12 months postpartum, it is no longer considered the normal, temporary hormonal shift (acute telogen effluvium) and is now classified as chronic telogen effluvium or is likely caused by an underlying condition unmasked by pregnancy.
Here is a step-by-step guide on what you should do:
Step #1: Consult a Specialist (Dermatologist)
The absolute first step is to see a board-certified dermatologist or a specialized trichologist, as they are experts in diagnosing hair loss conditions
The specialist will perform an exam and order specific blood tests to rule out the most common underlying triggers:
- Thyroid Function Tests (TFTs): To check for postpartum thyroiditis (hyper- or hypothyroidism), which is a major, yet treatable, cause of chronic shedding.
- Ferritin and Iron Studies: To check for iron deficiency (anemia). Low iron stores (ferritin) are a very common cause of hair loss in women, especially after pregnancy and blood loss from delivery.
- Vitamin D and B12 Levels: To check for other common nutritional deficiencies that impact hair follicle health.
- Hormone Panel: To check for other hormonal imbalances, such as those related to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
- Scalp/Hair Analysis: They may perform a simple Pull Test or a Trichometric Analysis to assess the severity, or in rare cases, a scalp biopsy to check for scarring or inflammatory conditions.

Step #2: Implement Targeted Treatment
The treatment will depend entirely on the confirmed diagnosis from your specialist.
| Confirmed Cause | Treatment & Action |
| Nutrient Deficiencies (Low Iron/Ferritin, Vitamin D) | Take prescription-strength supplements (e.g., high-dose iron/ferritin) to restore levels, combined with dietary changes. Do not self-supplement iron without a doctor’s guidance. |
| Thyroid Disorder | Treatment will focus on bringing your thyroid hormone levels back into balance, usually with medication. Once stabilized, hair regrowth typically occurs. |
| Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL) Unmasked | This is a genetic thinning often accelerated by the postpartum shift. Topical Minoxidil (Rogaine) is the most common FDA-approved over-the-counter treatment that stimulates follicles. Doctors may also prescribe oral medications like Spironolactone (anti-androgen) for women. |
| Chronic Stress/No Identifiable Cause | The focus is on removing the stressor and promoting growth. Treatment often includes low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices or Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) injections, which stimulate blood flow and growth factors in the scalp. |
Step #3: Sustained Lifestyle Management
Regardless of the medical diagnosis, maintaining a supportive environment for your hair is crucial for recovery.
- Prioritize Stress Reduction: Chronic, unmanaged stress can continue to perpetuate hair loss. Try to incorporate regular gentle exercise, meditation, or finding support groups.
- Optimal Nutrition: Continue a balanced diet rich in protein, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to ensure your hair follicles have the building blocks they need.
- Gentle Hair Care: Continue to avoid tight hairstyles (buns, ponytails) and minimize the use of heat styling (blow dryers, straighteners) to prevent breakage.
*The most important takeaway is this: When hair loss is chronic, it requires a medical diagnosis. Do not simply wait for it to stop, as it may be a sign of a treatable medical condition.
Should I Get Hair Transplant After Pregnancy?
Answer: NO, NOT IMMEDIATELY. YES, IF PERMANENT THINNING PERSISTS.
Navigating the postpartum period brings many changes, and for many women, one of the most concerning is postpartum hair loss. If you are considering a hair transplant to restore thinning areas or a receding hairline, the question of when to proceed is critically important for a successful outcome.
1. The Postpartum Hair Loss Timeline: Why Timing is Everything
The sudden, excessive hair shedding that new mothers experience often 3 to 6 months after delivery is known as telogen effluvium. This condition is caused by the dramatic drop in estrogen levels after childbirth, and it is almost always temporary.
If you rush into a hair restoration procedure while this temporary shedding is still happening, you face two potential issues:
- Inaccurate Graft Placement: Your surgeon may place grafts in areas where your natural hair would have eventually regrown, making the surgery partially unnecessary.
- Shock Loss Risk: The stress of the procedure could potentially trigger further shedding of the newly recovering hair surrounding the transplant site.
2. The Recommended Waiting Period for Hair Restoration
Specialists in female hair transplant surgery universally recommend a significant waiting period. The optimal time to pursue a FUE or DHI hair transplant is:
- Wait 12 Months Post-Delivery: This full year allows your hormones to stabilize and gives your hair follicles sufficient time to complete the growth cycle and revert to their pre-pregnancy fullness.
- Wait Until Weaning is Complete: If you are breastfeeding, you must wait until you have finished, as the medications used during and after the surgical procedure (anesthetics, antibiotics, and pain relievers) could be passed to the baby.
Key Takeaway: Do not schedule your hair transplant until your temporary postpartum hair loss has fully resolved. You want a stable baseline for your surgeon to accurately assess the extent of any permanent hair loss.
3. Preparing for Your Consultation
Once you have passed the 12-month mark, your next step is a consultation with a qualified hair transplant specialist. Be prepared to discuss:
- Your pregnancy and delivery details.
- The start and stop dates of your hair shedding.
- Any current or past nutrient deficiencies (such as iron or Vitamin D), which can impact the success of your hair transplant results.
By prioritizing stability and waiting for your body to fully recover from childbirth, you ensure the best possible foundation for a successful and lasting hair restoration procedure.
Advanced Surgical Hair Restoration Techniques for Postpartum Women
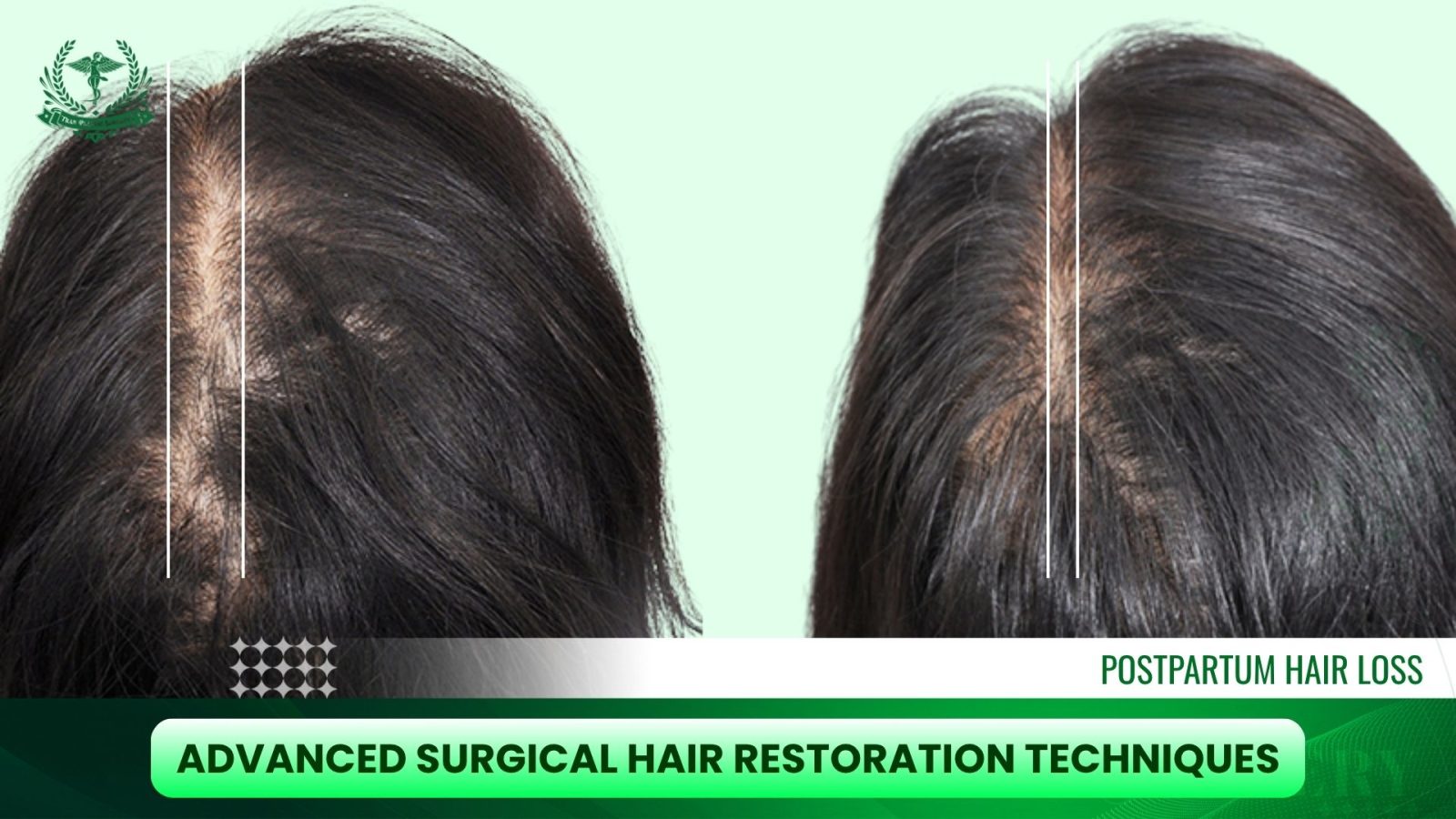
Hair transplant surgery is generally only considered if permanent hair loss (like female pattern baldness) is diagnosed and persists 12 months or more after delivery and weaning. The advanced techniques are known for creating the most natural-looking results with minimal scarring.
| Technique | Method | Key Advantage for Women |
| FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) | Individual follicular units are extracted using a micro-punch and then manually implanted into pre-made incisions. | Highly versatile, minimal scarring (tiny dots), and efficient for covering larger areas if needed. |
| DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) | Follicular units are implanted immediately after extraction using a specialized tool called a Choi Implanter Pen. | Highest precision in angle, direction, and depth; often allows for unshaven (or partial-shaven) procedures, which is ideal for women who want to keep the procedure discreet. |
Why DHI is Often Preferred for Women
While both FUE and DHI are effective, DHI is frequently favored by women because it offers:
- Discreet Recovery: By avoiding the full head shave, it significantly reduces the visible evidence of the procedure.
- Precision: It is excellent for rebuilding the highly visible frontal hairline with natural density and angle.
The decision between these surgical techniques depends heavily on the extent of the hair loss, the texture of your hair, your budget, and the surgeon’s expertise. When looking for the most natural and meticulous results, seek out a clinic with recognized expertise in aesthetic procedures, such as Tran Plastic Surgery, which employs board-certified surgeons specialized in the precise art of hair restoration.
Does Tran Plastic Surgery Perform Hair Transplants for Postpartum Women?
Yes. Tran Plastic Surgery offers customized hair transplant solutions for postpartum women who continue to experience significant or permanent hair thinning after pregnancy. Led by Dr. Tuan Tran, a board-certified plastic surgeon with extensive experience in advanced hair restoration, our clinic provides safe, ethical, and effective treatment options for women struggling with postpartum hair loss that does not resolve naturally within a year.
Why Choose Tran Plastic Surgery?
- Expertise in female and postpartum hair restoration
- Safe, sterile environment using the latest surgical technologies
- Personalized treatment plans tailored to hormonal balance and scalp condition
- Natural, long-lasting results with minimal downtime
If your postpartum hair loss persists beyond a year, you may be a candidate for a hair transplant after pregnancy. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Tuan Tran at Tran Plastic Surgery to discuss safe and effective solutions for restoring your confidence and natural hair density.