At Tran Plastic Surgery, we specialize in the diagnosis, treatment, and recovery of distal radius fractures, the most common type of broken wrist injury. Whether caused by a fall, accident, or weakened bone density, these fractures can be painful and limiting. With expert surgical and non-surgical options, our team ensures patients regain mobility, strength, and function with the highest standards of care.
What Is a Distal Radius Fracture?
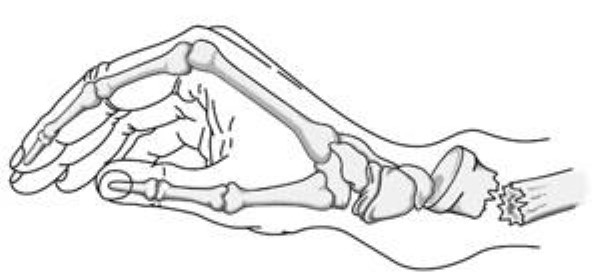
The radius is one of the two major bones in the forearm, and the distal radius refers to the end of the bone closest to the wrist joint. A distal radius fractures occurs when this area breaks, often leading to pain, swelling, and limited wrist movement.
This type of fracture is highly common across all age groups but is particularly frequent in older adults due to osteoporosis and in active individuals following high-energy trauma like sports or vehicle accidents.
Types of Distal Radius Fractures
Not all wrist fractures are the same. Proper classification is critical in determining the best treatment plan:
-
Colles Fracture – the most common type, where the broken fragment tilts upward.
-
Intra-Articular Fracture – extends into the wrist joint, making treatment more complex.
-
Extra-Articular Fracture – does not involve the joint surface.
-
Open Fracture – the broken bone pierces through the skin, requiring urgent surgical care.
-
Comminuted Fracture – the bone shatters into multiple pieces.
-
Displaced Fracture – bone fragments shift out of alignment.
In some cases, patients may also sustain a fracture of the distal ulna, the smaller bone in the forearm, further complicating treatment.
Causes of Distal Radius Fractures
The most common causes include:
-
Falls – especially landing on an outstretched arm.
-
Osteoporosis – weakened bones break more easily, even from low-impact falls.
-
High-impact trauma – such as car accidents, sports injuries, or biking accidents.
-
Age-related vulnerability – individuals over 60 often experience fractures from relatively minor incidents.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Typical signs of a distal radius fracture include:
-
Sudden, sharp pain in the wrist
-
Swelling and bruising around the joint
-
Tenderness to the touch
-
The wrist appearing bent or deformed
-
Inability to grip or move the hand normally
If the wrist looks visibly misaligned or the fingers become numb or pale, immediate medical evaluation is critical.
How Distal Radius Fractures Are Diagnosed
A thorough physical examination and X-rays are essential to determine the extent of the fracture, whether bones are displaced, and how many fragments are present.
In mild cases, waiting until the next day to see a doctor may be acceptable, but patients with severe pain, numbness, or deformity should seek emergency care immediately.
Treatment Options
The goal of treatment is to restore normal alignment and stability of the wrist while allowing bones to heal properly. The best approach depends on the fracture type, patient age, activity level, and bone quality.
Nonsurgical Treatment
If the bones remain in a stable position:
-
A cast or splint may be used to immobilize the wrist until healing is complete.
-
If bones are misaligned but can be corrected without surgery, a closed reduction procedure may be performed to manually realign them before casting.
-
Casts are typically worn for 6 weeks, with X-rays taken to monitor healing progress.
After removal, physical therapy helps restore motion and strength.
Surgical Treatment
When fractures are unstable or involve joint surfaces, surgery may be required. Surgical approaches include:
-
Open reduction with internal fixation (ORIF): Plates and screws are used to secure the bone fragments.
-
External fixation: A stabilizing frame outside the body holds bones in place.
-
Metal pins: Often used for temporary stabilization.
For open fractures, urgent surgery is necessary within hours to clean the wound, prevent infection, and stabilize the bone.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Every patient’s recovery varies depending on injury severity and treatment approach. In general:
-
Pain Management: Ice, elevation, and over-the-counter medications often suffice, though prescription pain relievers may be used short-term.
-
Cast & Wound Care: Keeping casts or surgical incisions clean and dry is essential.
-
Rehabilitation: Finger motion should begin immediately; wrist stiffness typically improves within 1–2 months after cast removal.
-
Return to Activity:
-
Light activities after 1–2 months
-
Sports and vigorous activities after 3–6 months
-
Full recovery can take up to 1 year, with gradual improvement continuing for 2 years.
-
Potential Complications
While most patients heal well, complications may occur, including:
-
Persistent stiffness or reduced mobility
-
Nerve compression or tingling in the hand
-
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), a rare but painful condition
-
Post-traumatic arthritis, especially in intra-articular fractures
Close follow-up with your surgeon minimizes risks and ensures the best long-term outcome.
Why Choose Tran Plastic Surgery for Distal Radius Fractures Care?
At Tran Plastic Surgery, we provide specialized orthopedic and reconstructive care tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Tuan Tran is highly experienced in managing complex wrist injuries, offering advanced surgical techniques and comprehensive rehabilitation plans to restore function.
We also treat other hand conditions, including:
For an overview of our expertise, visit our Hand Surgery services page.
Take the Next Step Toward Recovery
If you suspect a distal radius fractures or are seeking expert care after a wrist injury, don’t delay treatment. Early evaluation and proper management significantly improve recovery and long-term function.
📞 Call us today at 714-839-8000 or contact us online to schedule a consultation with our hand surgery team at Tran Plastic Surgery in Huntington Beach, CA.