Scaphoid fracture treatment requires specialized care to ensure proper healing and prevent long-term complications. At TranPlastic in Huntington Beach, our experienced hand surgeons provide comprehensive treatment for scaphoid fractures, from diagnosis through recovery, helping patients restore wrist function and return to daily activities.
What Is a Scaphoid Fracture?
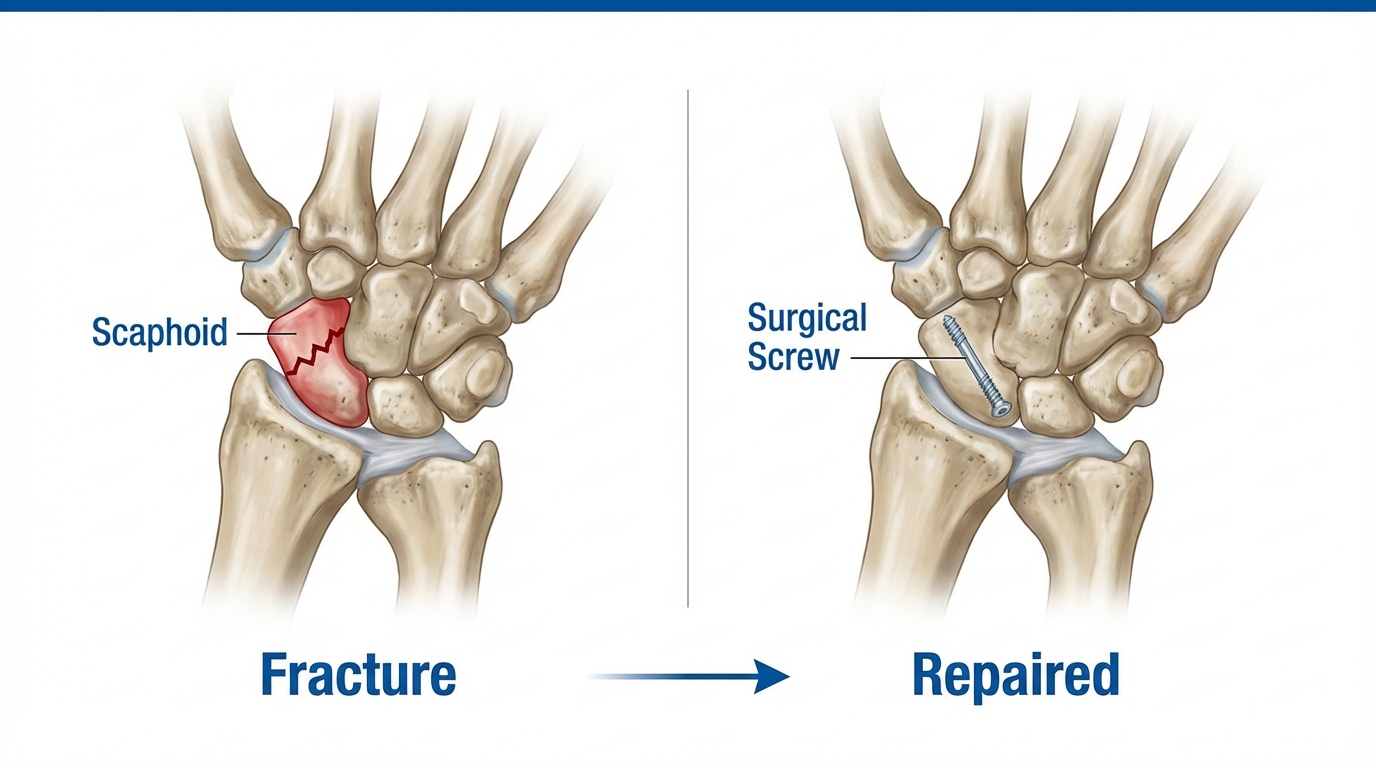
A scaphoid fracture is a break in the scaphoid bone, one of the small carpal bones in your wrist located near the base of your thumb. This type of fracture typically occurs when you fall onto an outstretched hand, and it requires prompt, specialized treatment to heal properly.
Common symptoms of scaphoid fracture:
- Pain and tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist
- Swelling near the base of the thumb
- Difficulty gripping or pinching objects
- Pain when moving the wrist or thumb
- Bruising around the wrist area

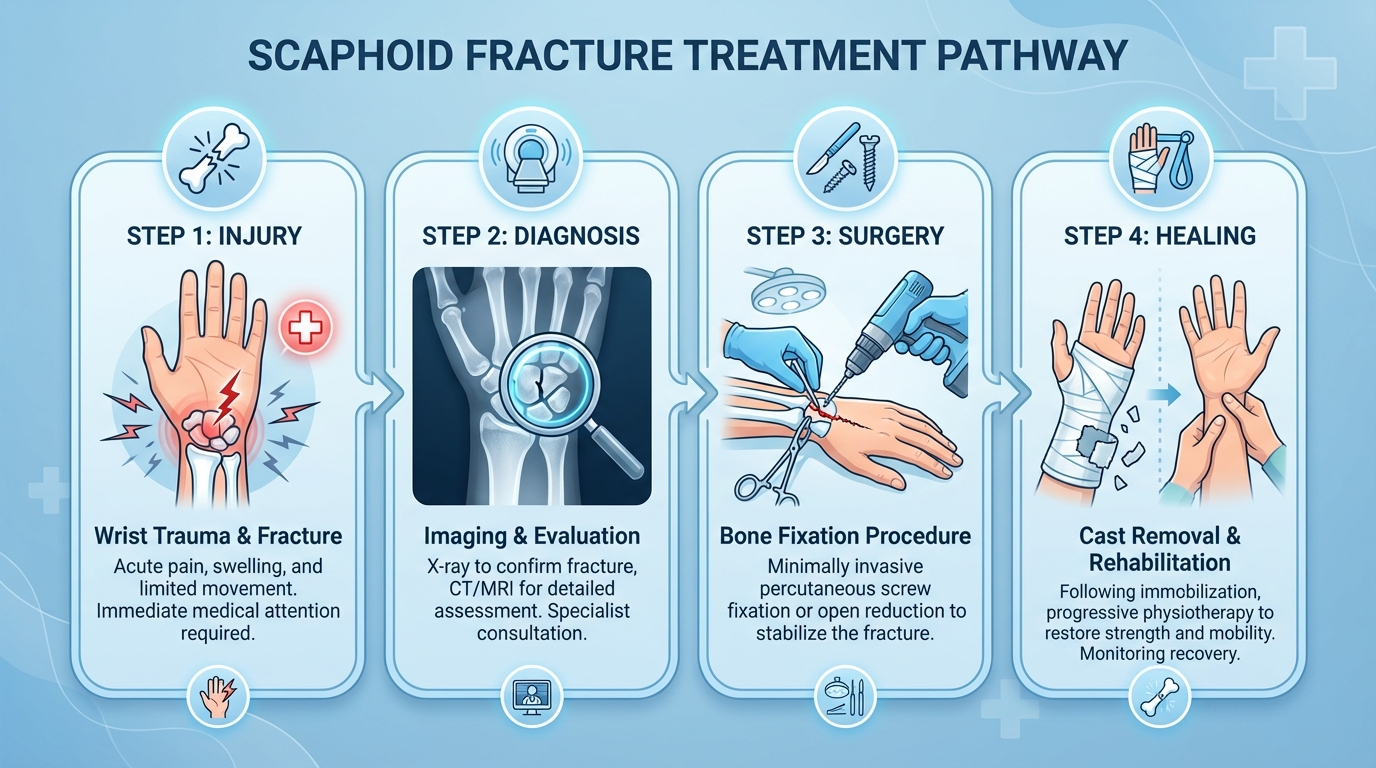
Scaphoid Fracture Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the location and severity of the fracture. Our specialists provide both non-surgical and surgical options:
Non-Surgical Treatment
For fractures near the thumb (distal pole) that are stable and properly aligned:
- Immobilization: Cast or splint for 6-12 weeks
- Regular monitoring: X-rays to ensure proper healing
- Activity modification: Avoiding activities that stress the wrist
Surgical Treatment
For displaced fractures or fractures in the middle of the bone (waist) that may not heal well with casting:
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF): Surgical realignment with screws or pins
- Minimally invasive techniques: Smaller incisions for faster recovery
- Bone grafting: For fractures that have not healed (nonunion)
Recovery Timeline
- Weeks 1-6: Cast immobilization. Keep wrist elevated and dry.
- Weeks 6-12: Transition to removable splint. Begin gentle range of motion exercises.
- Months 3-6: Progressive strengthening exercises. Gradual return to activities.
- Month 6+: Full recovery with restored wrist strength and mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my wrist is fractured or just sprained?
Scaphoid fractures cause pain specifically on the thumb side of the wrist, often with tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox. Only an X-ray or MRI can confirm a fracture. If you have persistent wrist pain after a fall, seek medical evaluation.
Can a scaphoid fracture heal without surgery?
Yes, if the fracture is non-displaced and located near the thumb (distal third), immobilization in a cast for 6-12 weeks often leads to successful healing. However, fractures in the middle of the bone have a higher risk of nonunion and may require surgery.
What happens if a scaphoid fracture is left untreated?
Untreated scaphoid fractures can lead to nonunion (failure to heal), avascular necrosis (bone death due to poor blood supply), and post-traumatic arthritis. These complications can cause chronic pain, weakness, and limited wrist function.
How long before I can return to sports after scaphoid fracture surgery?
Return to sports typically occurs 3-6 months after surgery, depending on the sport and individual healing. Contact sports or activities requiring heavy wrist use may require longer recovery. Your surgeon will clear you based on X-ray evidence of healing and strength testing.
Does scaphoid fracture treatment require physical therapy?
Yes, physical therapy is often recommended after cast removal or surgery to restore range of motion, strength, and function. Our team coordinates with physical therapists to ensure optimal recovery.
About Dr. Tuan Tran
Dr. Tuan Tran brings specialized training in hand and wrist surgery, offering advanced treatment for scaphoid fractures. With a focus on preserving long-term wrist function, Dr. Tran uses the latest techniques to ensure optimal outcomes for every patient.
Insurance & Cost
Scaphoid fracture treatment is typically covered by insurance. We work with most major providers and offer transparent pricing for self-pay patients. Contact us to verify your coverage.
Locations We Serve
Main Location: Huntington Beach, CA
Serving Orange County including: Newport Beach, Fountain Valley, Westminster, Garden Grove, Costa Mesa, Seal Beach
Contact Us
Experiencing wrist pain after a fall? Contact TranPlastic today for expert evaluation.
Phone: 714-839-8000
Contact Page: Tran Plastic Surgery Contact Page