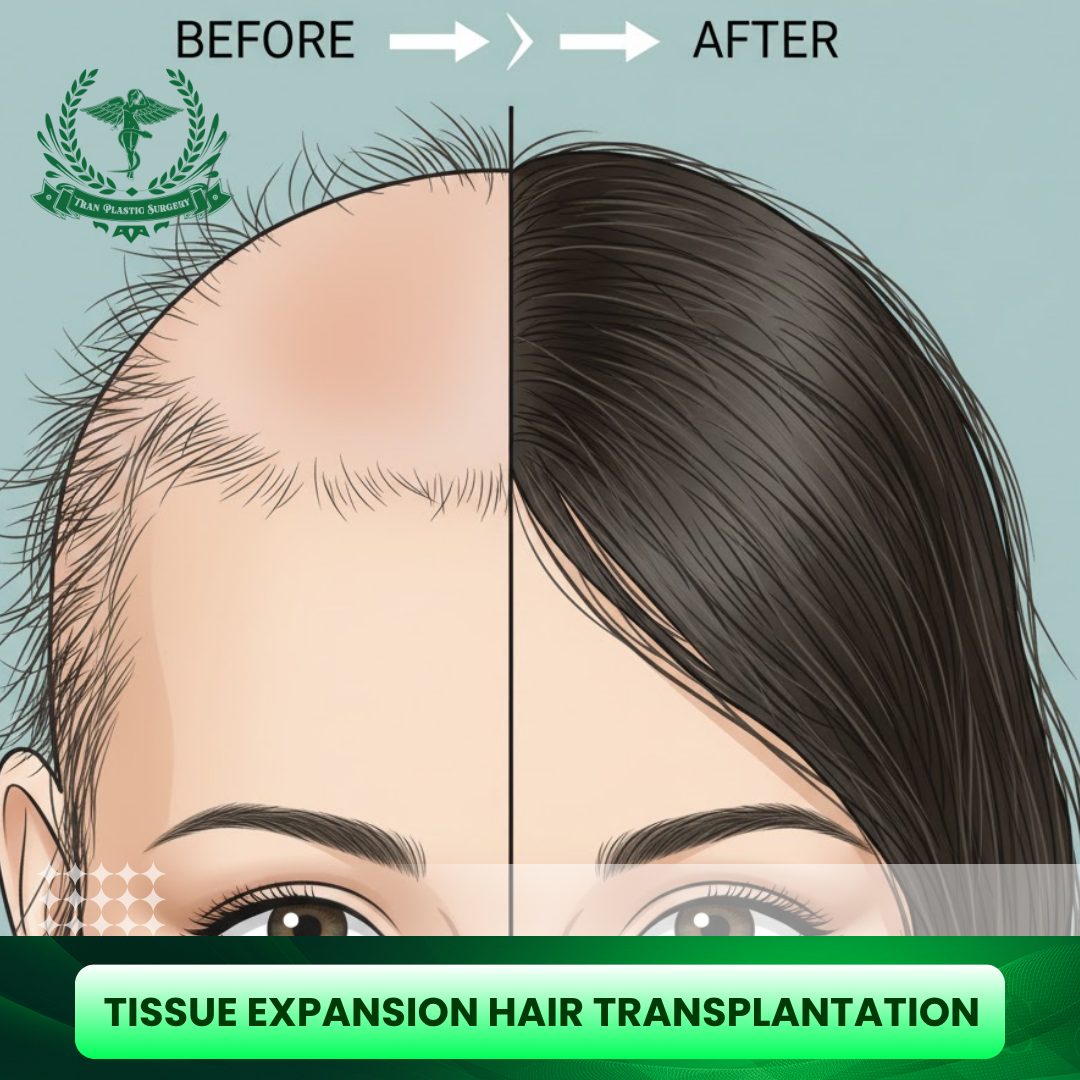
Tissue expansion hair transplantation is a breakthrough solution for people struggling with severe hair loss, scars, or scalp damage but few truly understand how it works or why it delivers such dramatic results. This advanced technique uses your own healthy scalp to regrow natural hair in areas once thought impossible to restore. In this guide, you’ll discover how tissue expansion transforms damaged skin into hair-bearing areas, who it’s best for, and why it’s becoming one of the most innovative options in modern hair restoration.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Tissue Expansion Hair Transplantation?
Tissue expansion hair transplantation is an advanced surgical technique in the field of hair restoration and reconstructive surgery. Unlike conventional methods such as FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) or FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation), which rely on relocating individual follicular units, tissue expansion uses the body’s natural ability to grow extra skin over time.
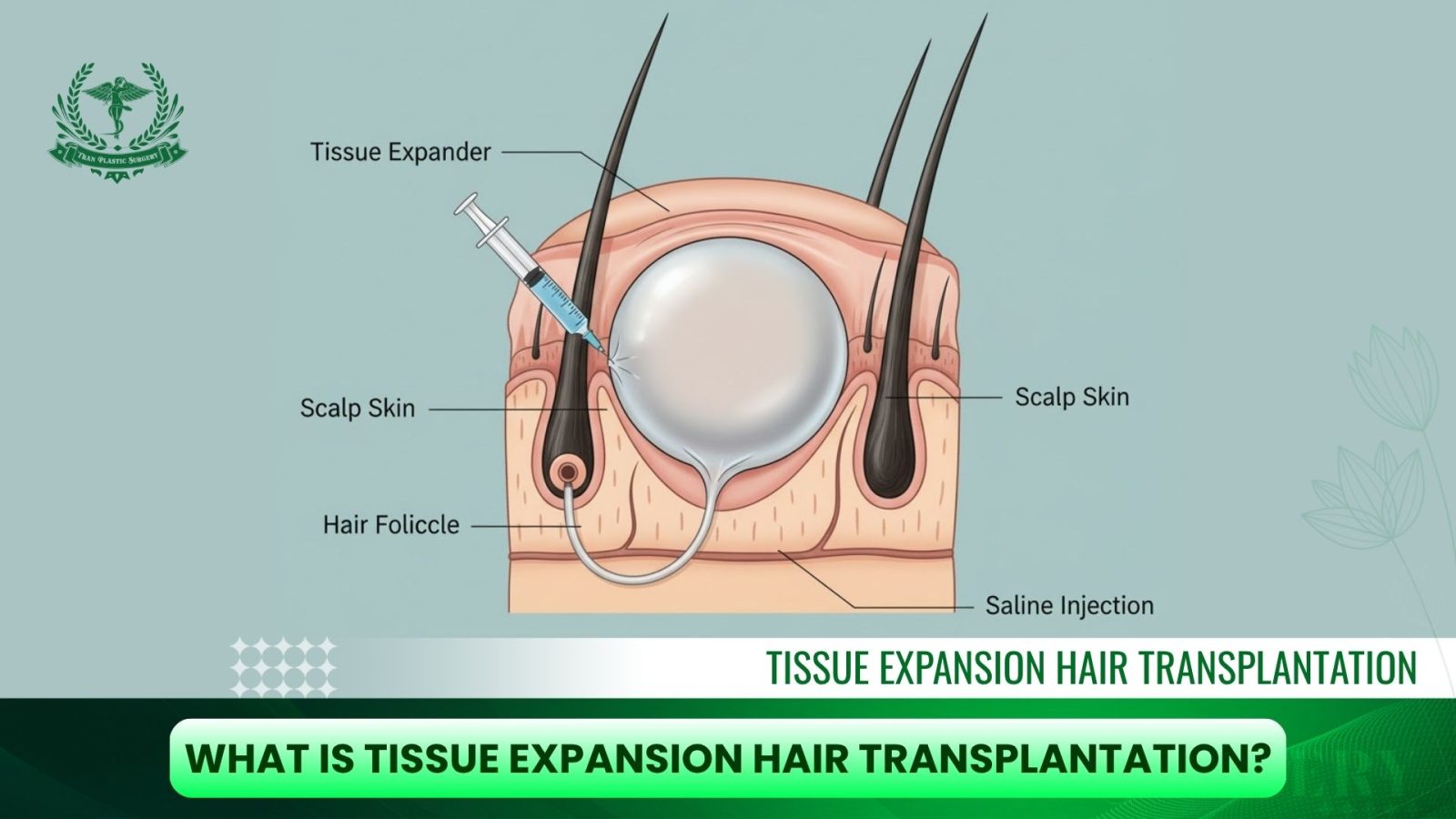
At the heart of this procedure is a tissue expander, a balloon-like silicone device that is surgically inserted beneath healthy, hair-bearing areas of the scalp. Over a period of weeks to months, this expander is slowly filled with saline solution, gently stretching the skin and prompting the body to produce new tissue that contains hair follicles.
Once a sufficient amount of new scalp skin has been generated, the expander is removed in a second surgery. The newly expanded skin, which now has its own naturally growing hair, is carefully rotated, advanced, or repositioned to cover bald or scarred regions of the scalp. The result is a seamless, natural appearance, since the transplanted area is composed of the patient’s own hair-bearing scalp rather than isolated grafts.
How Tissue Expansion Hair Transplantation Works
Tissue expansion hair transplantation is a multi-stage procedure that unfolds over several weeks to months. It is more complex than standard hair transplant surgeries, but it offers unique benefits for patients with large bald areas or scalp scarring. The process typically involves three major stages:
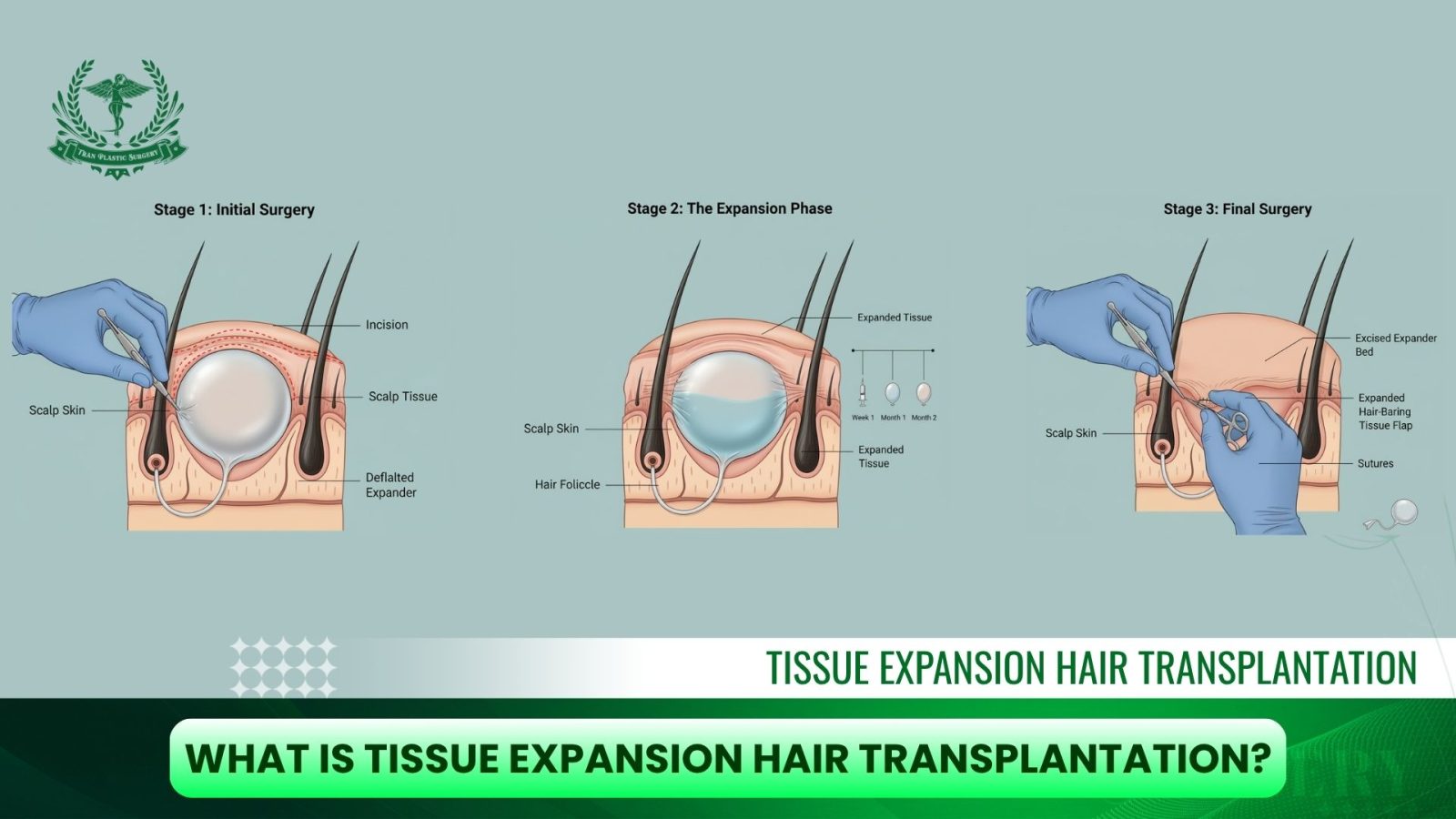
Stage #1: Implantation Surgery (Placement of the Expander)
The first stage focuses on preparing the scalp and placing the tissue expander:
- Incision and Pocket Creation: The surgeon makes a small incision in the healthy, hair-bearing portion of the scalp (often at the sides or back, where hair growth is strongest). A pocket is carefully created beneath the skin.
- Insertion of the Expander: A silicone balloon device, known as the tissue expander, is inserted into the pocket under the scalp tissue. This device contains a small self-sealing valve that allows controlled filling with saline in the weeks ahead.
- Closure: Once the expander is in place, the incision is closed with sutures. Patients are usually able to go home the same day, with some mild soreness or swelling expected.
At this stage, the expander is empty or only partially filled. The main goal is to place it safely without creating too much pressure on the scalp.
Stage #2: Expansion Phase (6–12 Weeks on Average)
This is the most critical part of the process, as the scalp is gradually stretched to generate new skin:
- Saline Filling: Over the course of 6–12 weeks, the surgeon periodically injects saline solution into the expander through its hidden valve. This is usually done once a week in the clinic.
- Gradual Stretching: As the expander fills, it slowly inflates beneath the skin, gently stretching the surrounding scalp. This stretching stimulates the body to grow new skin tissue, complete with functioning hair follicles.
- Patient Experience: During this phase, patients may notice tightness, mild discomfort, or temporary swelling in the treated area. These sensations are expected and typically subside as the scalp adjusts.
- Visible Changes: As expansion continues, the treated area may look unusual or swollen, but this is a normal part of the process. The payoff is that the body creates a significant amount of extra hair-bearing scalp, which becomes the foundation for the final stage.
Stage #3: Reconstruction Surgery (Advancing the Expanded Skin)
Once enough new skin has been generated, the expander is removed and the scalp is reshaped:
- Removal of the Expander: The surgeon reopens the incision, carefully removes the balloon device, and prepares the expanded tissue for repositioning.
- Reshaping and Coverage: The newly expanded, hair-bearing scalp is then rotated, advanced, or repositioned to cover bald, scarred, or defective areas. This step is customized to each patient’s needs, sometimes large bald patches can be completely closed using this method.
- Securing the Tissue: The repositioned scalp is stitched into place, ensuring both stability and a natural alignment with surrounding hair. Over time, the scalp heals, and the new hair-bearing area blends seamlessly with the rest of the head.
The key advantage of this technique is that the newly transplanted area already contains natural, functioning hair follicles. Unlike traditional graft-based transplants, which rely on individually moving hair units, tissue expansion creates full-thickness skin with hair, resulting in:
- Natural density and texture that matches surrounding areas.
- Permanent growth, since the transplanted skin retains its original characteristics.
- The ability to cover large bald or scarred regions in a way that conventional hair transplant methods often cannot achieve.
Benefits of Tissue Expansion Hair Transplantation
Tissue expansion hair transplantation differs from conventional hair transplant techniques such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). While grafting methods work well for many patients, they often fall short in cases of severe baldness, scarring, or when large areas need reconstruction. Tissue expansion offers several unique advantages, making it the preferred choice in these challenging scenarios.
1. Natural Results With Seamless Integration
One of the greatest strengths of tissue expansion is the naturalness of the outcome. Since the procedure relies on the patient’s own hair-bearing scalp:
- The transplanted skin contains intact, functioning hair follicles, ensuring hair growth looks and feels identical to the surrounding scalp.
- Hair grows at the same angle, density, and texture, avoiding the unnatural or “pluggy” appearance that can sometimes result from older grafting techniques.
- This is especially important for patients who want to restore not only coverage but also aesthetic harmony with their natural hairline.
2. Large Area Coverage for Severe Hair Loss
For patients with extensive baldness, traumatic injuries, or burn scars, tissue expansion is one of the few methods that can provide adequate coverage:
- Traditional hair grafting methods transplant follicles one by one, which can be limiting when thousands are needed.
- Tissue expansion, on the other hand, generates large patches of new skin, capable of covering bald regions that might otherwise require multiple surgeries with grafting alone.
- This makes it ideal for patients with cicatricial alopecia (scarring alopecia) or those who have lost scalp tissue due to accidents or surgeries.
3. Minimal Visible Scarring
Another major advantage is the reduced risk of obvious scarring:
- Because the technique uses the patient’s own skin, there is no need to make large donor incisions like in strip harvesting.
- The expanded skin is taken from an adjacent scalp area, which means scars are usually hidden within hair-bearing regions.
- Compared to older “flap” surgeries, tissue expansion leaves fewer visible marks, allowing patients to wear their hair in natural styles without worrying about surgical traces.
4. Long-Term Durability and Stability
Unlike hair grafts, which may thin or fall out over time, tissue expansion uses full-thickness scalp skin with intact vascular supply and follicular units. This means:
- The results are generally permanent.
- The transplanted area resists further hair loss progression because the follicles maintain their original genetic programming.
- Patients can enjoy stable hair density without requiring frequent touch-ups.
5. Psychological and Functional Benefits
Beyond the cosmetic improvements, tissue expansion provides significant emotional and functional gains:
- Patients with scarring or congenital defects often regain confidence as their scalp looks more natural.
- Restoring hair to a previously bald or scarred area can improve not only appearance but also protection of the scalp skin from sunburn or injury.
- For burn survivors and reconstructive patients, the procedure is often life-changing, offering both aesthetic recovery and emotional healing.
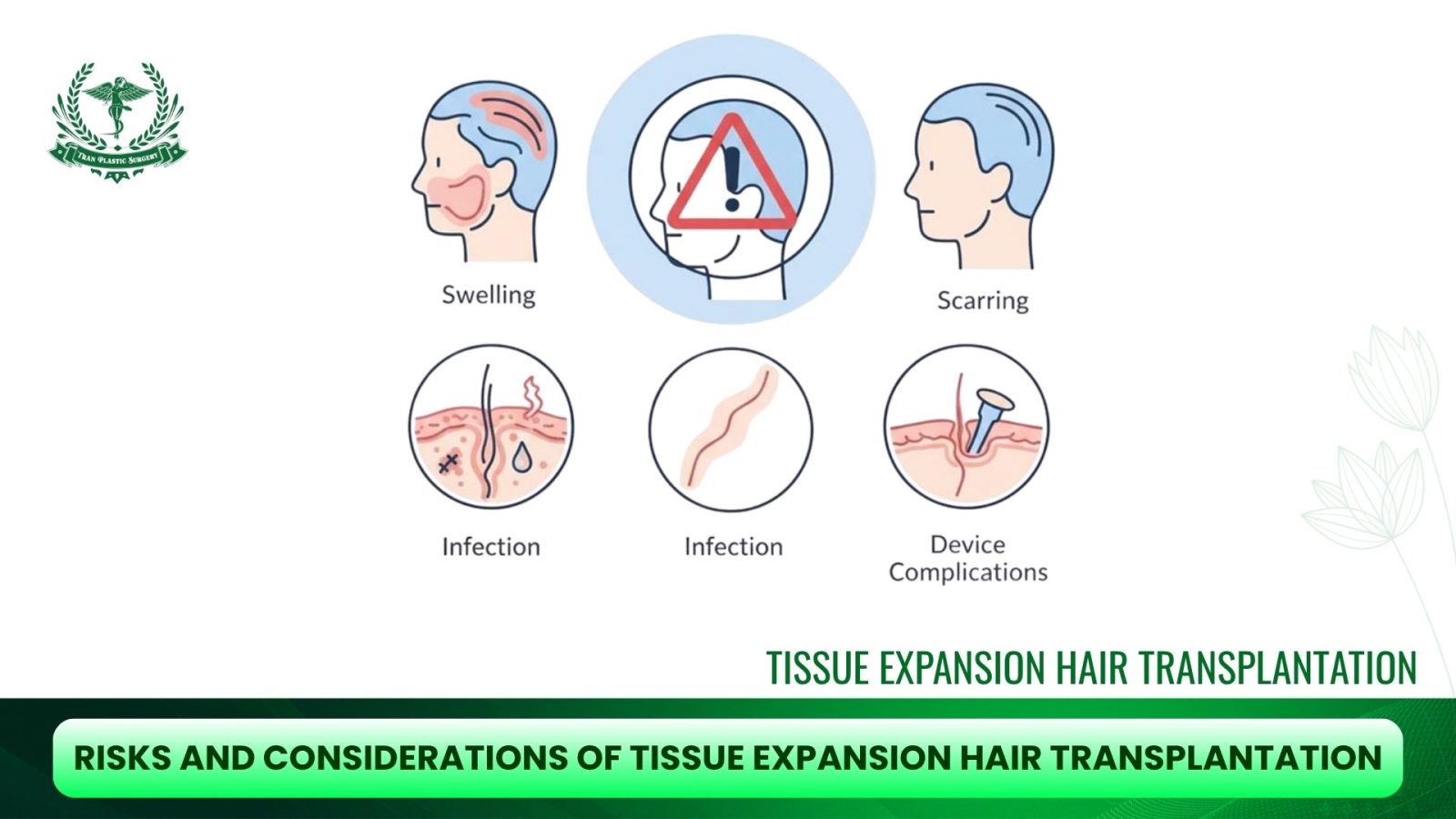
Risks and Considerations
While tissue expansion hair transplantation offers impressive results, it is important to understand that the procedure is complex and invasive, requiring careful planning, skilled surgical execution, and patient commitment. Like all surgical interventions, it carries risks, side effects, and limitations that must be considered before making a decision.
1. Multiple Surgeries Are Required
Tissue expansion is not a one-time procedure. It involves at least two major surgeries:
- First surgery – implanting the tissue expander under the scalp.
- Second surgery – removing the expander and repositioning the expanded hair-bearing skin.
Some patients may even require additional revisions if the area is large, or if complications occur. This makes the process longer and more demanding compared to standard FUE or FUT transplants.
2. Discomfort and Lifestyle Adjustments
During the expansion phase (6–12 weeks), the scalp is gradually stretched as saline is injected into the tissue expander. Patients may experience:
- Tightness and pressure in the scalp.
- Pain or discomfort after each filling session.
- Visible bulging in the scalp, which can be cosmetically noticeable and may cause social or emotional stress.
This temporary but challenging stage requires patience and commitment.
3. Potential Complications
Although generally safe when performed by an experienced surgeon, complications may include:
- Infection: As with any implanted device, there’s a risk of infection around the expander.
- Expander leakage or rupture: The silicone balloon may leak saline or fail, requiring replacement.
- Skin thinning or breakdown: Excessive expansion can compromise blood supply, leading to necrosis or poor healing.
- Expander extrusion: In rare cases, the device can push through the skin if the tissue becomes too thin.
- Scarring: Although minimized compared to older techniques, scars can still occur around the incision sites.
Close monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to detect and manage issues early.
4. Longer Recovery and Downtime
Compared to conventional hair transplant procedures, tissue expansion requires longer healing periods:
- Recovery from the first surgery may take 1–2 weeks before normal activities can resume.
- The expansion phase itself lasts several weeks to months, during which the patient must attend frequent appointments.
- After the second surgery, downtime can extend again for several weeks, depending on healing and complexity.
Patients should plan for a more prolonged timeline before seeing their final results.
5. Patient Selection Matters
Not everyone is an ideal candidate for tissue expansion hair transplantation. Factors that influence suitability include:
- Donor site availability: Patients must have enough healthy, hair-bearing scalp to expand.
- Scalp elasticity: Poorly elastic skin may not stretch effectively.
- Medical conditions: Patients with uncontrolled diabetes, clotting disorders, or poor wound-healing capacity may face higher risks.
- Age and lifestyle factors: Smoking, poor nutrition, or chronic illness can negatively affect healing outcomes.
A thorough consultation with a plastic surgeon or hair restoration specialist is critical to determine whether this procedure is appropriate.
6. Psychological and Emotional Considerations
Because the expansion device causes visible bulging of the scalp, patients may feel self-conscious during the treatment period. This can temporarily affect social interactions, work, or personal confidence. Surgeons often recommend strong emotional preparedness before committing to the process.
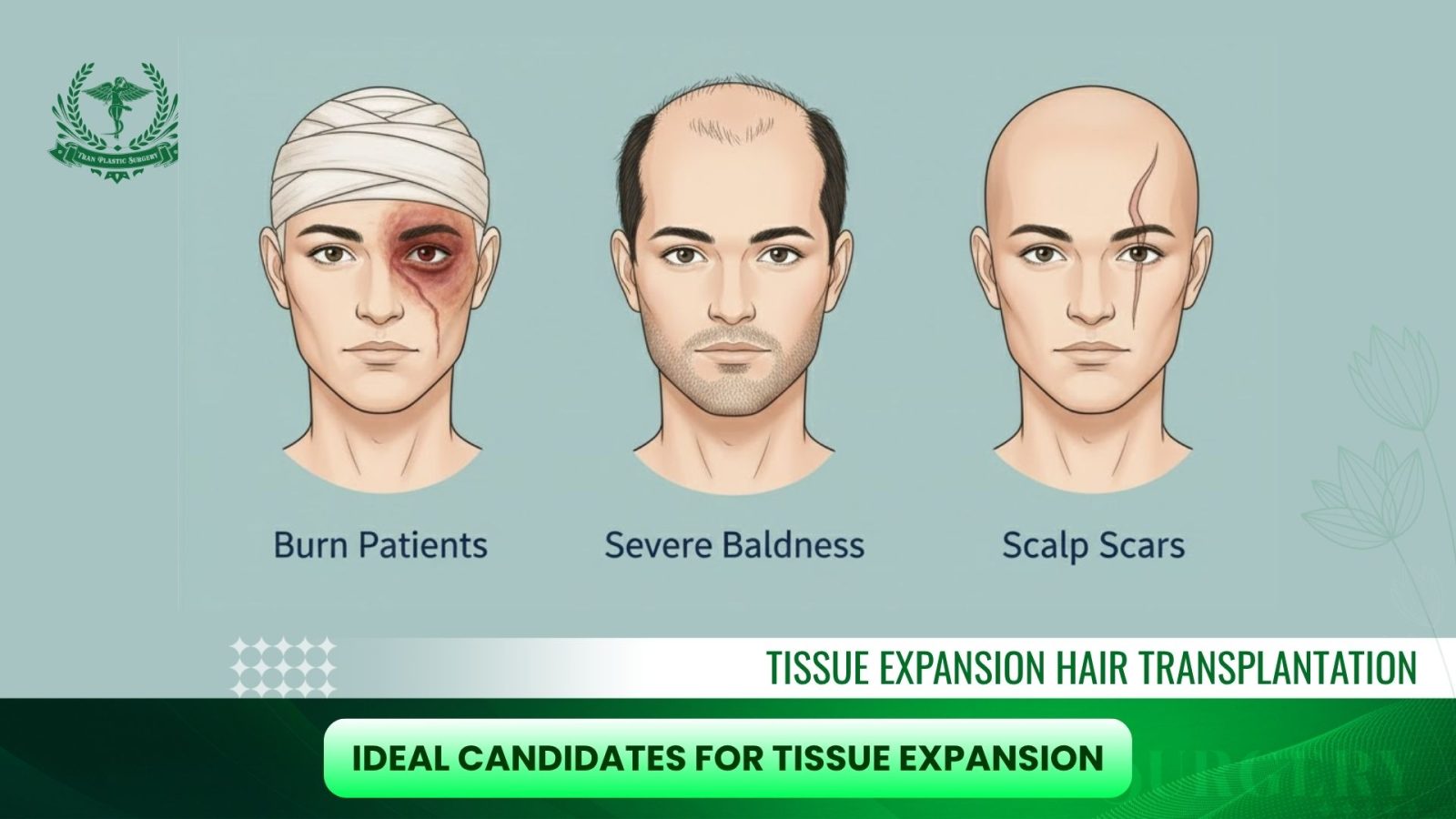
Ideal Candidates for Tissue Expansion
Not every patient experiencing hair loss is suited for tissue expansion. Because this method is more invasive than traditional follicular unit extraction FUE or FUT, it is generally reserved for complex or advanced cases of hair loss.
1. Common Candidate Profiles
- Patients with Scalp Burns or Trauma-Related Scarring
- Individuals who have suffered accidents, fire burns, or previous surgical scars often lose both skin and hair follicles.
- Tissue expansion creates new, healthy scalp tissue with active follicles, which can be rotated into the damaged area for a natural restoration.
- Individuals with Extensive Baldness Beyond FUE/FUT Capacity
- Standard hair transplantation methods (like FUE or FUT) rely on donor follicles. In patients with very limited donor hair, grafts may not be enough.
- Tissue expansion offers a way to cover large areas of baldness using full-thickness, hair-bearing scalp, achieving results that grafting alone cannot.
- Patients with Cicatricial (Scarring) Alopecia
- Conditions like lichen planopilaris or discoid lupus can destroy hair follicles and leave permanent scarring.
- Expanded tissue provides new scalp skin that is resistant to further hair loss, offering a more stable long-term solution.
- Patients Prepared for Multi-Stage Surgery
- Tissue expansion requires commitment and patience. Candidates must accept multiple surgeries, weeks of expansion, and extended recovery.
- Individuals who understand the process and are mentally prepared for the temporary aesthetic changes (like scalp bulging) are better positioned for success.
2. Who May Not Be Suitable?
- Patients with poor scalp elasticity that cannot accommodate expansion.
- Individuals with insufficient donor hair or widespread thinning.
- Patients with serious medical conditions (uncontrolled diabetes, clotting disorders, immune system compromise) that impair healing.
- Those unwilling or unable to commit to the long recovery process and multiple procedures.
Cost of Tissue Expansion Hair Transplantation
Tissue expansion for hair transplantation is a specialized and multi-stage procedure, so its cost is not typically quoted on a per-graft basis like other hair transplant methods. Instead, it’s often priced as a complete surgical package due to its complexity and the multiple appointments required.
- United States: Tissue expansion for hair restoration is a major reconstructive procedure and can be quite expensive. While per-graft pricing for other methods might range from $5 to $7, the total cost for tissue expansion is typically a flat fee for the entire procedure. Some sources indicate a range of $9,000 to $19,000 USD for scalp tissue expansion in the United States and the United Kingdom.
- Other Countries: For medical tourism, some countries offer more competitive rates. For example, in Australia, costs might range from $7,800 to $16,500 USD, while in Thailand, the cost can be between $4,500 and $8,000 USD. India offers some of the most affordable options, with costs ranging from $2,500 to $6,000 USD.
At Tran Plastic Surgery, Dr. Tuan Tran will design individual treatment plans, and the final price will depend on the specific needs and complexity of each patient. Patients should also consider additional costs such as anesthesia, follow-up visits, and possible revisions. (Applicable to new surgical methods today)
Tissue Expansion Hair Transplantation Recovery Timeline
| Phase | Duration | What to Expect |
| Initial Surgery | 1 day | The tissue expander is surgically placed. You may experience some swelling and discomfort. |
| Expansion Process | Weeks to Months | You will have regular appointments to gradually fill the expander with saline. A noticeable bulge will form on the scalp. |
| Final Surgery | 1 day | The expander is removed, and the newly stretched scalp is advanced to cover the bald area. |
| Immediate Post-Op | 1-7 Days | Swelling and bruising are common. You will have bandages and should rest. |
| Early Recovery | 1-2 Weeks | Sutures or staples are typically removed. You can resume gentle hair washing. Avoid strenuous activity. |
| Shock Loss | 1-3 Months | The transplanted hair will shed. This is a normal part of the process and indicates a new growth cycle. |
| Early Hair Growth | 4-6 Months | Fine, new hairs will begin to emerge. |
| Significant Growth | 6-12 Months | The new hair will thicken and gain density. Final results will become apparent. |
| Full Recovery | 12-14 Months | The transplanted hair is fully mature, and any scars have faded. |
Final Thoughts
Tissue expansion hair transplantation is a powerful solution for individuals facing severe hair loss or scalp scarring. Although it requires multiple stages and a longer recovery compared to traditional hair transplants, the natural, permanent, and large-scale results make it an excellent choice for suitable candidates. If you are considering advanced hair restoration options, consult with a board-certified plastic surgeon experienced in tissue expansion.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Tuan Tran at Tran Plastic Surgery to explore whether tissue expansion hair transplantation is the right solution for your hair restoration journey.