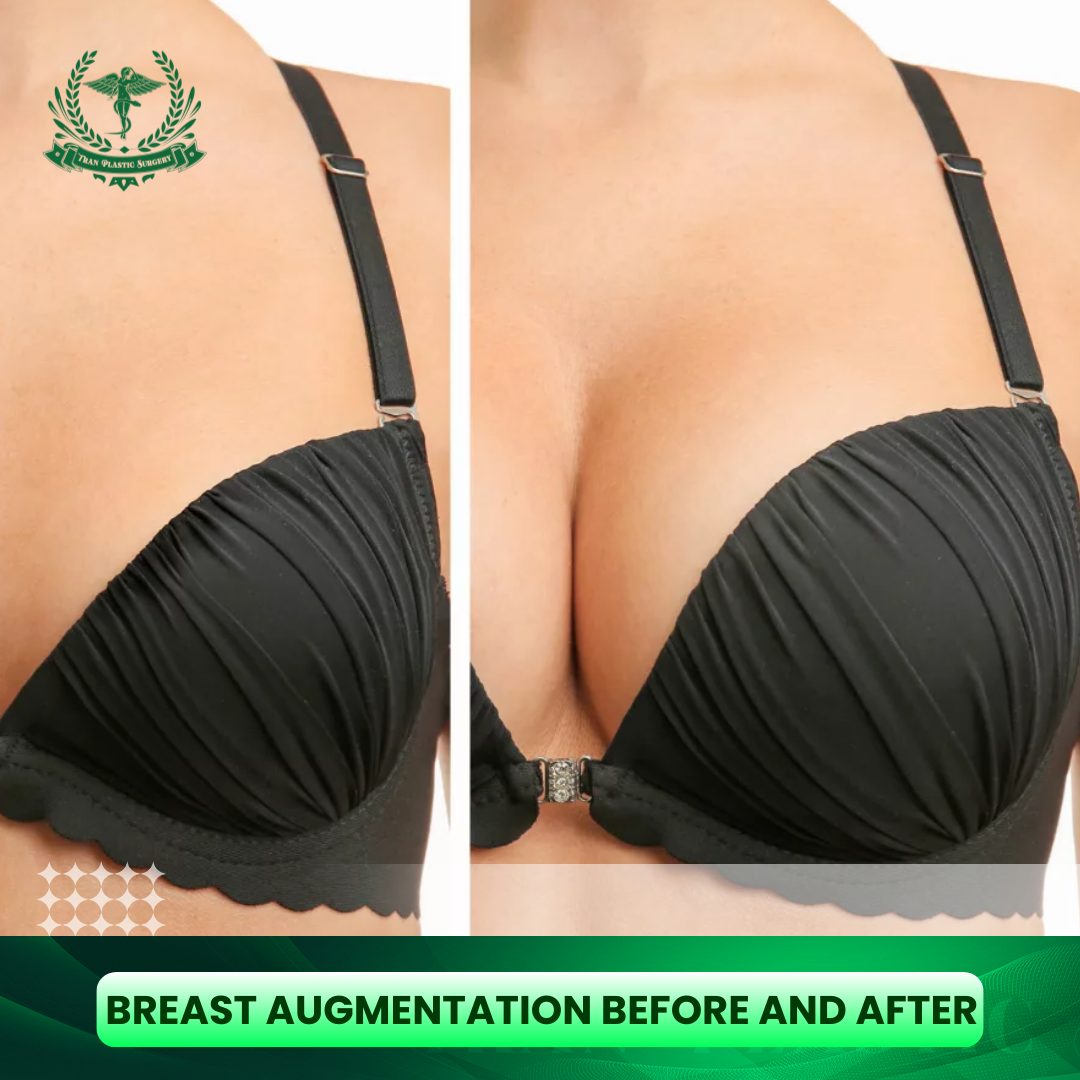
Table of Contents
ToggleCommon Causes of Hair Thinning in Men and Women
When patients ask, “Why am I losing hair?”, the answer often depends on multiple overlapping factors. Hair thinning can develop gradually or appear suddenly, depending on your genetics, hormone levels, lifestyle, and even certain medications. Understanding these root causes is essential before considering any treatment plan.1. Genetic Hair Loss (Androgenetic Alopecia)
The most frequent cause of hair thinning in both men and women is androgenetic alopecia, also known as pattern hair loss. This condition is hereditary, meaning it runs in families, and is influenced by hormones called androgens.- In men, it typically appears as a receding hairline and thinning at the crown.
- In women, it presents as a general reduction in hair density, especially at the top and sides of the scalp.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
Fluctuations in hormones play a major role in hair health. Many women experience hair thinning after pregnancy, during menopause, or due to thyroid disorders. Elevated levels of androgens or an imbalance in estrogen can disrupt the natural growth cycle, leading to increased shedding or finer strands. For men, testosterone and its byproduct dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can weaken hair follicles over time, resulting in progressive thinning.3. Stress and Emotional Factors (Telogen Effluvium)
Periods of physical or emotional stress such as illness, surgery, childbirth, or psychological strain can trigger a condition called telogen effluvium. In this state, a large number of hairs enter the resting phase simultaneously, leading to noticeable shedding a few months later. Fortunately, this type of hair loss is usually temporary once the underlying stressor resolves, but ongoing stress may prolong or intensify the thinning process.4. Nutritional Deficiencies
Healthy hair growth depends on adequate nutrition. Low levels of iron, vitamin D, zinc, or protein can weaken hair follicles and reduce strand quality. People following restrictive diets or experiencing digestive issues that limit nutrient absorption are particularly vulnerable. A simple blood test can help identify deficiencies and guide dietary or supplement-based correction.5. Medical Conditions and Medications
Certain health conditions including autoimmune disorders such as alopecia areata, scalp infections, or chronic illnesses can result in partial or widespread hair loss. Medications for blood pressure, depression, birth control, or chemotherapy may also contribute to hair thinning as a side effect. If you notice sudden or patchy loss, consulting a qualified medical professional is essential to determine whether the cause is systemic or medication-related.6. Hair Care Practices and Styling Damage
Daily habits can also influence hair health. Frequent use of hot tools, tight hairstyles, harsh chemical treatments, or extensions can weaken hair shafts and irritate the scalp. Over time, this can cause traction alopecia, a preventable form of hair loss caused by repeated tension on the roots. Gentle hair care, scalp-friendly products, and balanced styling routines are key to maintaining long-term hair strength. Hair thinning rarely stems from one single cause. Most patients experience a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Recognizing these patterns early is the best way to prevent further damage and plan appropriate treatment.
How to Identify Early Signs of Hair Thinning
Recognizing the early warning signs of hair thinning can make a significant difference in protecting your scalp health and preventing further loss. Many people overlook subtle changes until the problem becomes visible but by paying attention to certain symptoms, you can take timely action and explore effective treatments.1. Increased Hair Shedding
Noticing more strands on your pillow, shower drain, or hairbrush is often one of the first clues. While it’s normal to lose between 50 to 100 hairs per day, consistent shedding beyond this range may suggest that your hair growth cycle has been disrupted. If you’re asking yourself, “Why am I losing hair more than usual?”, track how frequently this happens over a few weeks.2. Gradual Reduction in Hair Volume
A decrease in hair density especially on the crown or along the part line is a hallmark sign of hair thinning. Women may see their ponytails becoming smaller in diameter, while men may notice that their scalp is more visible under bright light. This gradual loss of volume is typically associated with androgenetic alopecia or long-term hormonal changes.3. Widening Hair Part or Receding Hairline
A widening central part or receding temples often indicates pattern hair loss. In men, the hairline usually starts moving backward in an “M” shape. In women, the part line widens progressively, making the scalp more noticeable. These patterns help professionals diagnose the type and stage of thinning.4. Changes in Hair Texture or Quality
If your hair starts to feel finer, weaker, or breaks easily, it could be a sign that your follicles are producing thinner strands. Over time, this change in texture reduces overall fullness. Excessive chemical treatments or heat styling can worsen the issue, accelerating visible hair thinning.5. Sensitive or Itchy Scalp
Sometimes, scalp irritation, flakiness, or inflammation accompanies early hair loss. These symptoms may point to dermatological issues such as seborrheic dermatitis, fungal infections, or inflammation linked to follicle damage. A specialist can examine your scalp and recommend appropriate topical or medical solutions.6. Uneven Hair Growth
Hair that grows more slowly or irregularly across different scalp areas may signal that certain follicles are weakening. This uneven growth pattern can precede visible bald spots, so documenting it early through photos or professional scalp scans can help track progression.
Effective Treatments for Hair Thinning and Hair Loss
Once you’ve asked yourself, “Why am I losing hair?”, the next question naturally becomes, “What can I do about it?” The good news is that modern hair restoration science offers a wide range of solutions. From medical therapies that slow down shedding to advanced surgical procedures that restore density, there’s an effective option for nearly every cause of hair thinning.1. Topical and Oral Medications
For many patients, the first line of defense involves FDA-approved medications that help stabilize or reverse hair loss:- Minoxidil (Rogaine®): Applied directly to the scalp, it stimulates follicles to promote new growth and extend the hair’s active growth phase. It’s suitable for both men and women.
- Finasteride (Propecia®): A prescription pill used primarily for men, finasteride works by blocking the hormone DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which contributes to follicle shrinkage.
2. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP has become one of the most popular non-surgical treatments for hair thinning. During the procedure, a small sample of your blood is drawn, processed to concentrate the platelets, and then injected into thinning areas of the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that naturally stimulate follicle activity, improving hair density and thickness over time. Because PRP uses your body’s own plasma, the treatment is safe, minimally invasive, and requires little to no downtime. Regular sessions, typically spaced a few months apart, can help maintain long-term results.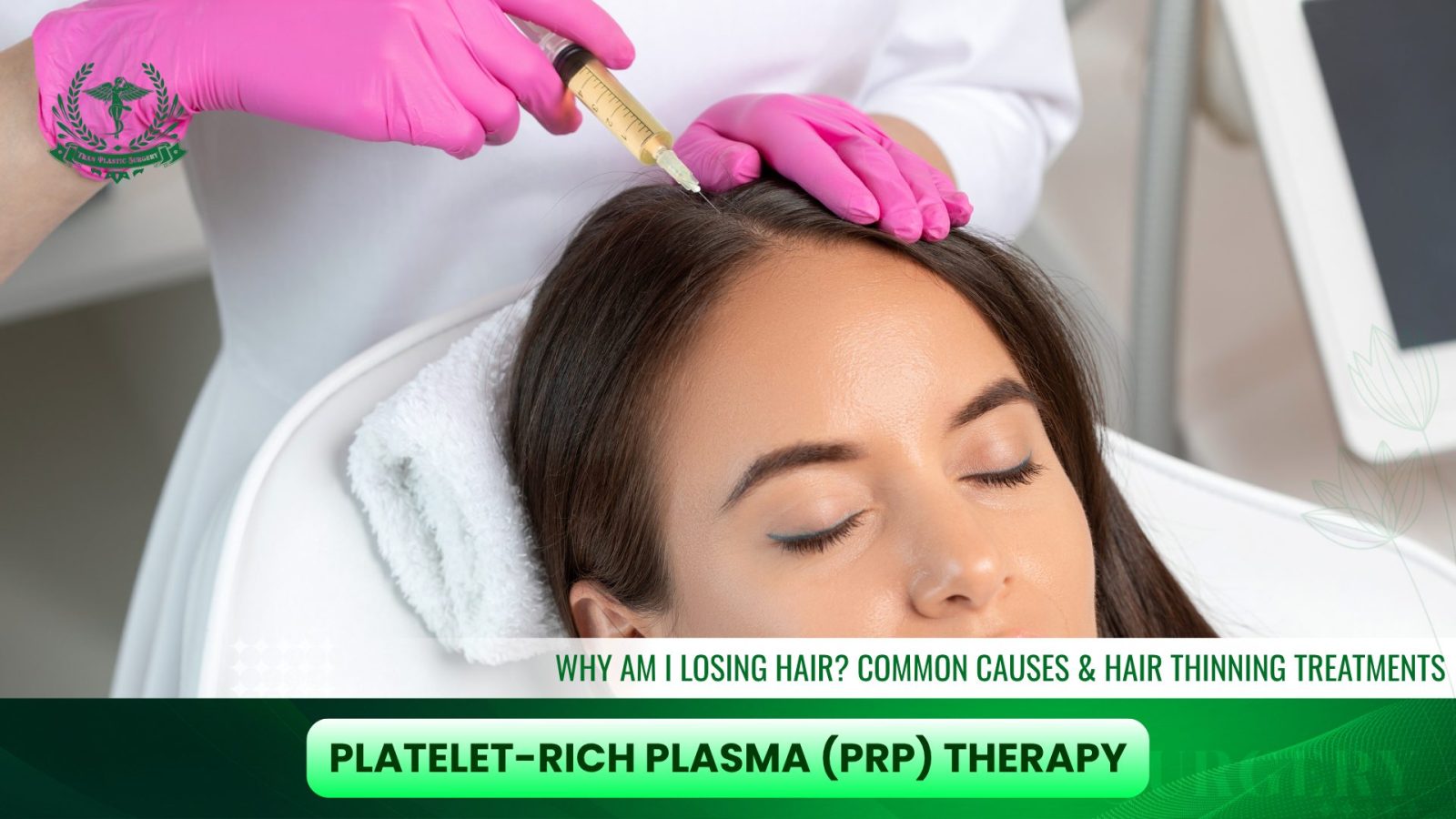
3. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Also known as laser light therapy, LLLT uses gentle, therapeutic light to boost blood circulation and energy production within the follicles. This can help reduce inflammation, improve scalp health, and support regrowth in mild to moderate hair thinning cases. It’s often recommended as a supportive treatment alongside medication or PRP to enhance outcomes.4. Nutritional and Lifestyle Support
Because diet, stress, and overall wellness play major roles in hair health, a comprehensive approach is always best. Nutritional supplements containing biotin, zinc, iron, and vitamin D can strengthen weak follicles. Additionally, managing chronic stress, improving sleep, and maintaining scalp hygiene all contribute to healthier, fuller hair. A medical professional can recommend a balanced plan tailored to your specific needs.5. Hair Restoration Surgery (FUE and FUT)
For more advanced hair thinning or pattern baldness, surgical restoration provides the most transformative and permanent results.- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual follicles are harvested from the donor area (usually the back of the scalp) and transplanted to thinning or bald zones. This technique leaves minimal scarring and offers a natural appearance.
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): In this method, a small strip of scalp is removed from the donor area, and follicular units are microscopically separated before being implanted. It’s ideal for patients needing large coverage.
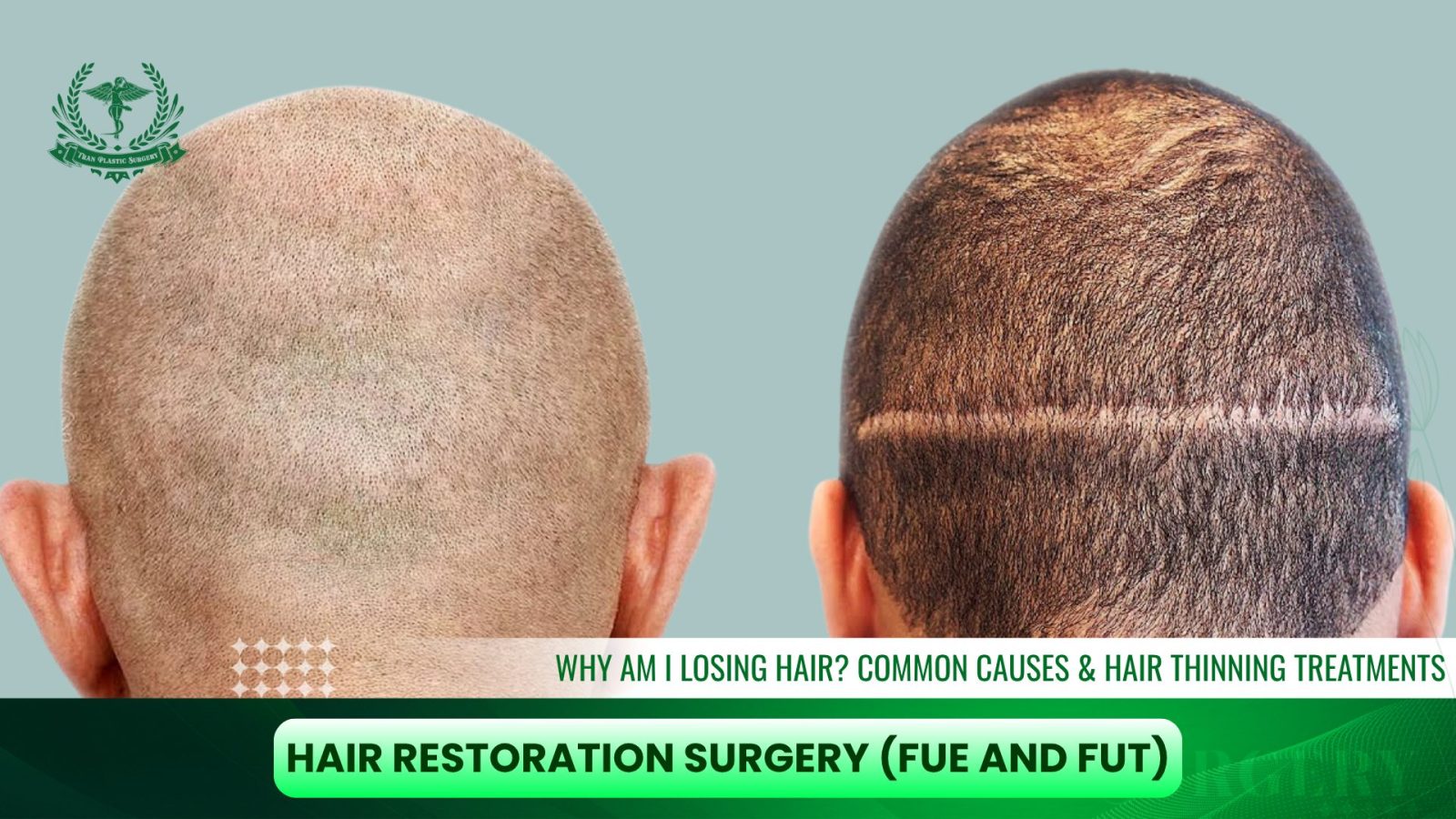
6. Combination Therapy and Ongoing Care
No single treatment fits every patient. In most cases, a personalized combination plan such as PRP sessions combined with topical medication or laser therapy delivers the most reliable outcomes. Regular follow-up visits help monitor progress, adjust protocols, and maintain results for years to come.How to Prevent Further Hair Thinning and Maintain Healthy Growth
While some causes of hair thinning like genetics can’t be completely prevented, healthy daily habits and early intervention can significantly slow the process and preserve your natural density. Here are the key strategies experts recommend:1. Protect and Nourish the Scalp
- Keep your scalp clean and balanced; buildup, excess oil, and inflammation can restrict follicle activity.
- Use mild, sulfate-free shampoos and massage your scalp regularly to stimulate blood circulation.
- Avoid scratching or over-exfoliating, as it can damage sensitive follicles.
2. Strengthen Hair Through Nutrition
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet with protein, iron, zinc, and vitamin D, all vital for hair growth.
- Include omega-3 fatty acids (found in salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds) to support scalp health.
- Consider supplements, but only under professional guidance to avoid overuse or imbalance.
3. Manage Stress Levels
- Chronic stress disrupts the hair growth cycle, often causing shedding known as telogen effluvium.
- Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, or regular exercise to stabilize hormone levels.
4. Avoid Damaging Hair Habits
- Limit frequent heat styling, bleaching, or chemical treatments that weaken the hair shaft.
- Avoid tight hairstyles like braids, ponytails, or extensions that pull on roots and can cause traction alopecia.
- Let your hair air-dry when possible and use gentle detangling methods.
5. Schedule Regular Scalp Checkups
- Monitor changes in density, shedding, or scalp sensitivity.
- Early evaluation by a hair restoration specialist helps detect potential issues before they worsen.
- Professionals can recommend tailored preventive treatments such as PRP maintenance sessions or laser therapy to keep follicles active.
6. Stay Consistent With Medical Treatments
- If prescribed topical or oral treatments like minoxidil or finasteride, use them exactly as directed.
- Discontinuing treatment abruptly can lead to renewed hair shedding.
- Combine therapies, strategically medication, PRP, and proper nutrition often yield the best long-term results.
Conclusion – Restore Your Hair, Renew Your Confidence
Worried about hair thinning or sudden shedding? You’re not alone and effective solutions are within reach. At Tran Plastic Surgery in California, we understand how personal hair loss can be. Our expert team tailors every plan to your needs, combining medical expertise with advanced technology for results that look completely natural.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Losing Hair and Hair Thinning
1. Why am I losing hair so suddenly?
Sudden hair loss often results from temporary disruptions in the hair growth cycle. Common triggers include stress, illness, hormonal changes, or nutritional deficiencies. This type of shedding called telogen effluvium typically improves within months once the underlying cause is addressed. However, if hair loss continues beyond six months, a medical evaluation is essential to rule out chronic conditions like androgenetic alopecia or thyroid disorders.
2. Is hair thinning normal as I get older?
Yes, mild hair thinning is a natural part of aging for both men and women. Hair follicles gradually shrink with age, producing finer strands. However, excessive thinning or visible scalp exposure is not normal and may indicate genetic or hormonal hair loss. Early preventive care can help preserve density and slow progression.
3. Can hair thinning be reversed?
In many cases, hair thinning can be improved or partially reversed with proper diagnosis and timely treatment.
Early-stage thinning often responds well to topical treatments, PRP therapy, or nutritional support.
Advanced cases may require hair restoration surgery, such as FUE or FUT transplants.
The sooner treatment begins, the higher the chance of stimulating new growth and restoring fullness.
4. How long does it take to see results from treatment?
Most patients notice visible improvement within three to six months, depending on the chosen therapy.
- Medications like minoxidil and finasteride require consistent daily use to maintain results.
- PRP and laser treatments often show progressive thickening after several sessions.
- Surgical transplants achieve full results within 9–12 months, as transplanted follicles establish new growth cycles.
5. How much does hair restoration cost in the United States?
The cost of hair restoration treatments in the U.S. varies widely depending on the method and extent of hair loss:
- PRP Therapy: $400 – $1,000 per session (typically 3–6 sessions recommended).
- FUE Hair Transplant: $4,000 – $15,000, depending on graft quantity and surgeon expertise.
- FUT Hair Transplant: $3,500 – $10,000, depending on the treatment area and clinic location.
Prices differ by city and provider, but always choose a board-certified plastic surgeon or hair restoration specialist to ensure safety and results.
6. When should I see a hair restoration specialist?
If you notice persistent shedding, receding hairlines, or thinning that doesn’t improve after lifestyle changes, schedule a consultation promptly. A qualified professional can perform a scalp analysis, identify the cause of hair loss, and recommend a personalized treatment plan to protect and regrow your hair.
7. Are hair restoration results permanent?
Surgical hair transplants provide long-lasting and often permanent results because transplanted follicles are genetically resistant to DHT, the hormone responsible for most pattern hair loss. However, ongoing care such as PRP maintenance, medication, and healthy scalp habits is crucial to preserve native hair and enhance long-term density.